A wise woman once sang “It’s not real if you don’t feel it”* and as far as the arts are concerned it’s as good a measure of quality as anything. But what is “it” that you are feeling? Is everyone feeling the same thing? Clearly not. Even the opinions of people who do like the same song, the same book, the same film, the same painting, are likely to diverge when it comes to the detail of what they like and how it feels.
*The Goonies “R” Good Enough, (Cyndi Lauper, Stephen Broughton Lunt, Arthur Stead, 1985
Part of the mission of modernism in the early 20th century was to free art from associations; from sentimentality, from tradition, culture, religion, politics – and to define it for itself. That was necessary, in order to break the endless repetitive staleness of academicism and/or lowest-common-denominator entertainment, and also because photography and recorded sound and near-universal literacy had all become significant factors in western society. Looking at the visual arts; if all that art does is to repeat what is already popular, to record and represent and recreate the visual and the actual, then how can it compare or compete with something like the camera which captures that external reality? And if that external reality, in the form of contemporary society, is something the artist rejects or objects to, then why use its tools and its language at all?
It’s hard to imagine, a century after the modernist explosion (say 1900-1939), the extent to which the arts were in thrall to academicism. Presumably that was because, having fought first for freedom from the world of manual labour and craftsmanship back in the late middle ages and renaissance period, later artists were keen to stress their respectability, their links to nobility, aristocracy and wealth. But access to that world came – not surprisingly – with rules, manners and forms of behaviour which settled, over the course of a couple of centuries, into rigid artistic traditions. Therefore, the artists of the modernist era were, like any revolutionaries, especially concerned with making their own manifestos and statements. ‘Art for art’s sake’ is a nineteenth century, essentially romantic/bohemian idea which feels remote from the milieu of modernism, but at the same time a theory of ‘pure art’ is found more clearly in something like Kazimir Malevich’s The Non-Objective World (1926) than in anything written by Théophile Gautier or Edgar Allen Poe;
“Art no longer cares to serve the state and religion, it no longer wishes to illustrate the history of manners, it wants to have nothing further to do with the object, as such, and believes that it can exist, in and for itself, without “things”.’

Though formulated later, this is the kind of theorising that helps partially to explain works like Malevich’s Black Square (1st version 1915). Un-controversially considered a masterpiece – and one that I myself like a lot – it nevertheless seems to me a work that gains enormously from some kind of context, even if all that context is, is the knowledge that it is in fact a painting by an artist. ‘Left to itself’, without any associations, if encountered ‘cold’, especially if it wasn’t in a gallery, it might just as easily not be ‘art’ at all. And while that isn’t a bad thing, a random black square encountered in one’s daily life doesn’t – depending of course on the individual who encounters it – have the intensity or pregnant quality that one can (repeat of previous caveat) feel standing in front of Malevich’s ‘Black Square’. But what Malevich does in his statement is to take the artist out of the art and anthropomorphise the art itself (“…it wants to have…”). This seems to me to negate – not unintentionally – what is meant by art at all. For myself, I prefer the German Expressionist Karl Schmidt-Rottluff’s statement which, while it doesn’t even slightly contradict the idea of purely abstract art, puts the artist at its centre, rather than treating art as a kind of self-creating phenomenon:

“I know of no new ‘programme’…. Only that art is forever manifesting itself in new forms, since there are forever new personalities – its essence can never alter, I believe. Perhaps I am wrong. But, speaking for myself, I know that I have no programme, only the unaccountable longing to grasp what I see and feel, and to find the purest means of expression for it.”
Karl Schmidt-Rottluff in Kunst und Kunstler (1914) quoted Wolf-Dieter Dube, The Expressionists, p.21 (T&H 1972, transl. Mary Whittall)
If a painting hangs in a forest…
The three key factors here (for me) are creator-work-recipient. If the artists (Schmidt-Rottluff’s ‘personalities’) are trying to communicate something specific to the recipient with their work, then they either succeed or they don’t. If the artist doesn’t succeed in communicating what they intended to communicate – or if they aren’t thinking of the ‘end user’ at all, and are expressing their own feelings/ideas purely for their own reasons – they may (and probably will) still transmit something of themselves; a personality, an emotion or group of emotions, a mood or idea. But although in either case the work may be imbued with that power, it only becomes power when someone else is there to experience and/or interact with it. In material terms, the great masterpieces of painting, be it the Mona Lisa (oil paint on wood), or the Black Square (oil paint on linen) have little more intrinsic ‘value’ than a few tubes of oil paint or a piece of wood or linen. After the lights go out and the visitors go home, those paintings basically cease to exist as art. The alchemy that takes place when art finds an audience is what makes it art; at least, so it seems to me.
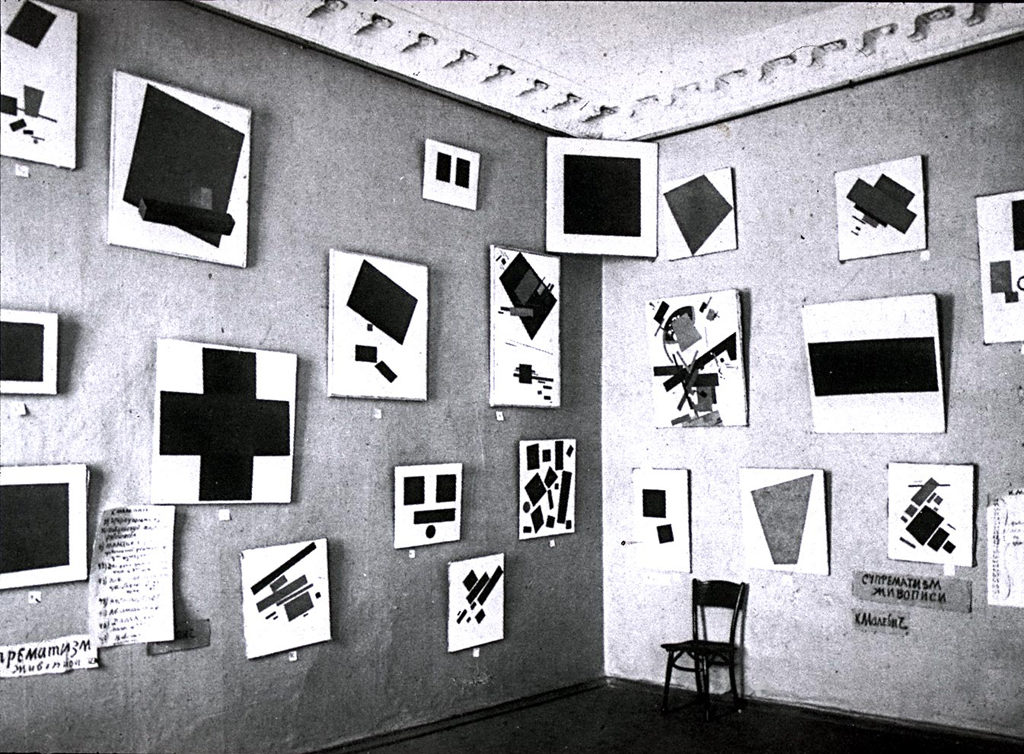

So can there be ‘good’ or ‘bad’ art? Short answer; intuition says yes, but experience says no. Alongside the disintegration of traditional academic rules, there has been the growth and persistence of the myth that, in order to break the rules of art, you must first understand and adhere to the rules. This idea has been strengthened by the fact that some of the iconic figures of modern art, like Picasso and Dali, have been immensely talented by the traditional, renaissance standards of art and could easily have made a career in academic painting; but so what? Would Guernica, looking exactly as it does, be a lesser work of art if it was the only painting Picasso had ever done, or if his immature works had been bland and unimpressive?
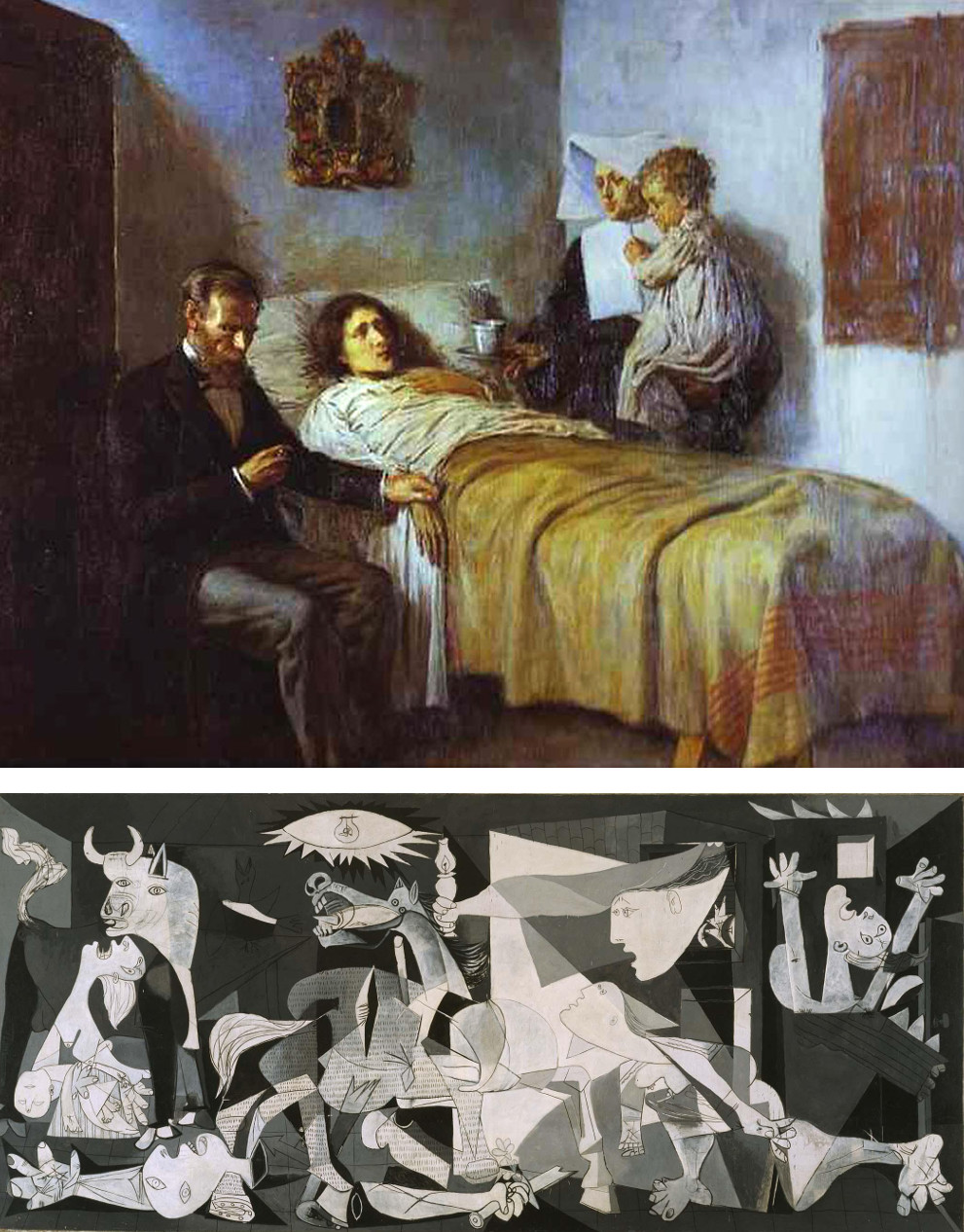
Bottom – Pablo Picasso – Guernica (1937)
Separating personal, aesthetic judgements of good and bad from objective judgements is almost impossible, A strong argument could be made for either one of the above images being ‘better’ than the other, especially since the emotional impact is entirely subjective. And separating these kinds of aesthetic judgements from moral ones can become even more complicated – can a work of art that is an expression of something ‘bad’ be good? If for example we discovered that Picasso was celebrating rather than mourning/protesting the slaughter and destruction at Guernica, would the painting be as good? And what does ‘good’ even mean in that sentence anyway? The idea that (for instance) a painting, or a song is “bad” is essentially meaningless, despite the fact that millions of paintings and songs are clearly very bad. They can never be demonstrably bad because, as Hamlet says, (and even the relatively short history of pop music proves) “there is nothing either good or bad, but thinking makes it so.” Even the most derivative, tuneless, unimaginative, moronic or amateurish song can and will be loved by someone, or many someones. And beyond people liking it, how can the quality of something like art truly be gauged? Yes, ‘liking’ can be a complex thing and is not the same as ‘admiring’ and yes, there are people with knowledge and expertise and highly developed critical faculties and so forth; but their opinion can no more prove a work of art is good than a restaurant critic can prove that a Michelin-starred chef’s finest creation tastes better than a Big Mac.
Despite the ‘golden ratio’ of the ancients, Hogarth’s ‘line of beauty’ and the Turner Prize, despite Grammys and Brits and Eurovision Song Contests, there is no logical ‘2 + 2 = 4’ type equation which can prove that “4” equals a good work of art. In architecture at least, a building either works as a building (ie it stands up and people can go inside) or it doesn’t, but even then, it would probably be easier to ‘prove’ that your local supermarket is logically ‘better’ as a building than Chartres Cathedral, rather than vice versa. But obviously (unless you are very lucky) it isn’t better than Chartres Cathedral. It feels too trite and easy to say ‘art is only as good or bad as an individual’s opinion of it’, but I can’t really do any better than that. You can’t make someone like something by telling them it’s good, however convincing your argument may be to you.
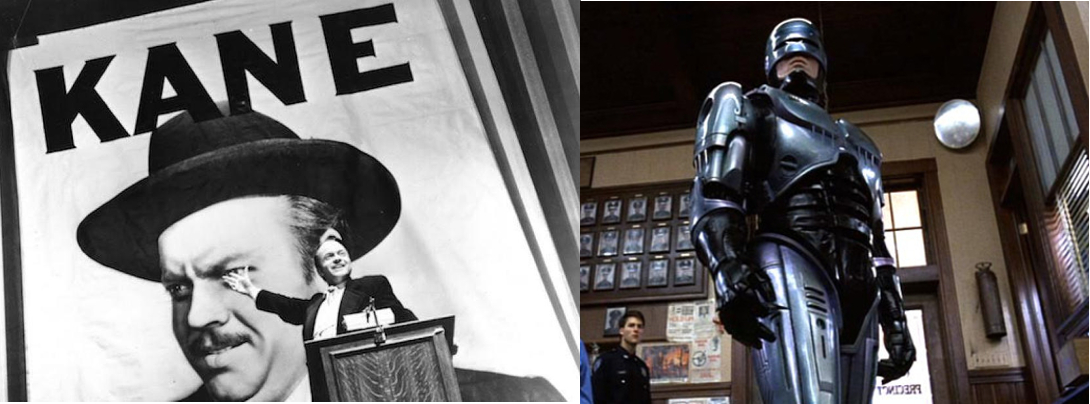
I also don’t think (though I am less convinced about this) there are good or bad reasons for liking a work of art, a song or a book, although there are certainly different levels of engagement. These are still subjective though; I like Citizen Kane but I love Robocop. Do I think Robocop is therefore the better film? Absolutely not. In the western world there is a kind of agreed pantheon of ‘great art’, codified by the way in which art history, English literature, cinema et al are taught in institutions and, at the lower end of the scale in books and websites of the corny ‘1000 albums/films you must hear/see before you die’ type, but in practice everybody constructs their own pantheon, with the ‘official’ ones being little more than a vague guide. I know that Robocop wouldn’t exist in the same form as it does without the innovations of Citizen Kane, but that doesn’t change the way I feel about either film. In reality, the only way to gauge (for example) the “greatest album ever recorded” is to have a public vote without offering a list of previously selected albums to choose from and then see who ‘wins’ – and I am sure I still wouldn’t agree with it.

Over the years, it has often been considered that the ‘correct’ critical attitude is to remove sentimentality from judgements on the arts. That is one way – judging pictures on their composition, harmony etc, ignoring subject altogether, evaluating music on its structure, technical skill etc – but it is sometimes almost impossible to do. And really, thinking again of both the emotional satisfaction people get from songs, films, pictures they love, and the example of Malevich’s Black Square, is it even desirable to do so? Thinking of Black Square – to judge a work which has so much context; theoretical, spiritual, cultural and emotional – by the sum of its basic physical attributes is reductive, as well as boring. Likewise, a great portrait in no way relies on the viewer knowing anything about the sitter, but even so – is Holbein’s great Henry VIII (1537) more interesting and engaging as flat masses of colour laid out in a particular, intricate design on a two-dimensional surface, or as the impression and interpretation of one human being through the eyes, mind and skill of another? The answer for me is the latter, which is really both, since the technical aspects of the first option are anyway incorporated in the second.
Pogo and the Black Square
A debate that rears its head fairly often – and I guess will increasingly do so as information about everything becomes more readily available – is whether ‘bad’ people (or just bad people) can make good art. Unlike art, and despite the murkiness of morality (influenced as it is by essentially amoral and anyway changeable concepts like tradition, religion and culture) there are some people that we can probably agree are bad, or at the very least, ‘not good’. Here’s an uncontroversial opinion; John Wayne Gacy, the ‘killer clown’, rapist and murderer of around 33 young people, was – even if he was at the mercy of his own personality disorder – a bad person. He also made something that is as close to being ‘bad art’ as anything I can think of. The fact that his paintings are collected by people and have sold for serious sums of money has nothing to do with their quality as art and everything to do with their associations. You could of course say much the same about the Black Square. And if the imaginary passerby who unpreparedly encountered the Black Square also encountered one of Gacy’s paintings, how would the experience differ?

Firstly, unlike the Black Square they would know immediately that Pogo the Clown was a painting made by a human being, and, if from a western background, they would probably recognise the subject matter. Because of this, Gacy is both at an advantage and disadvantage; an advantage because, no matter how the viewer feels about clowns, they have immediate ‘access’ to the painting – ‘I know what that is’. Disadvantage, because while the black square is a black square and therefore looks like a black square, Gacy’s clowns, portraits, skulls etc are – by the standards that most people judge art by – pretty amateurish. He wasn’t accomplished enough as an artist (I don’t mean just in a technical way) to communicate anything very deliberately. He wanted his paintings to bring joy into peoples’ lives; which seems unlikely, unless said people are serial killer fetishists or love clowns indiscriminately, so what the viewer is left with are essentially just his obsessions – or at least the ones he could express to his own satisfaction through his art.
Going back to my highly dubious creator-work-recipient idea of art, the creator, Gacy was (or said he was) trying to do something specific – to create bright and happy pictures to bring joy to the recipient. Whether he succeeded in this aim, regardless of who he was, depends on how one responds to childlike but sometimes enigmatic pictures of clowns. What he definitely did do was to transmit something of himself; a clear-cut but deeply alienated/alienating vision of the world; actually, without a world. His pictures don’t as one might expect, depict a simplified Norman Rockwell America, with the sun in the sky and a clown in the garden, but essentially just the clown; mostly in fact Pogo the clown, Gacy’s own alter ego, sometimes with an extremely cursory, but telling hint of a setting. Not a circus, or the suburbia of the childrens’ parties he haunted, but a hint of a dark, fairytale forest (the seven dwarfs appear in a particularly odd picture). These are clowns in the wild. The term ‘outsider art’ could have been coined for Gacy’s paintings. The other often-used term, ‘naïve art’ seems fleetingly appropriate, until one considers pictures like his paintings of Charles Manson, or even more so, of Tim Curry’s Pennywise from the TV adaptation of Stephen King’s IT. Gacy may not have been a good painter, he may have been to all intents and purposes insane, but he was not naïve; he knew that he belonged to a pantheon of famous murderers, that he was the original killer clown, and he was flattered by the association.
transmit something of himself; a clear-cut but deeply alienated/alienating vision of the world; actually, without a world. His pictures don’t as one might expect, depict a simplified Norman Rockwell America, with the sun in the sky and a clown in the garden, but essentially just the clown; mostly in fact Pogo the clown, Gacy’s own alter ego, sometimes with an extremely cursory, but telling hint of a setting. Not a circus, or the suburbia of the childrens’ parties he haunted, but a hint of a dark, fairytale forest (the seven dwarfs appear in a particularly odd picture). These are clowns in the wild. The term ‘outsider art’ could have been coined for Gacy’s paintings. The other often-used term, ‘naïve art’ seems fleetingly appropriate, until one considers pictures like his paintings of Charles Manson, or even more so, of Tim Curry’s Pennywise from the TV adaptation of Stephen King’s IT. Gacy may not have been a good painter, he may have been to all intents and purposes insane, but he was not naïve; he knew that he belonged to a pantheon of famous murderers, that he was the original killer clown, and he was flattered by the association.

But Gacy was chosen as an deliberately extreme example; even more extreme would be Hitler. Hitler’s serviceable but bland and slightly lifeless paintings are also highly collectable, despite lacking even the visceral ‘disturbed’ quality of Gacy’s. Whereas the innocent buyer might just be attracted to Gacy’s clowns for their kitsch, weird, outsider quality, Hitler’s works are best suited for what they were meant to be – postcards, unambitious souvenirs, illustrations. The lack of frisson they have as images is an indicator that the reasons people have for buying them have little to do with the pictures themselves. For, hopefully, a variety of reasons, these people are not buying ‘art’ at all, they are buying history.
The art didn’t abuse…
The world of actual ‘high’ art also has its fair share of murderers, rapists and so forth, and the question of whether their lives and actions invalidate their work is never really answerable. Apart from anything else, what about the legions of artists, musicians, writers whose private lives and opinions we know little or nothing about? Or artists like Andrea del Castagno, known for centuries as a murderer because of a mistake (whether malicious or not we cannot know) in Giorgio Vasari’s biography of him? At this distance of time it doesn’t really matter, even when talking about a definite murderer like Caravaggio. We don’t expect historical figures to have views, opinions and beliefs that we would find acceptable in the 21st century, although people of the 16th century certainly felt at least as strongly about murder as we do now.
When we get closer to our own time, things become more complicated. For me, it’s easy to disregard the achievements of, say Eric Gill*, because even without the knowledge of his child (and animal) abuse, his work isn’t really my cup of tea; graceful and stylish yes, but, given that he was a contemporary of people like Jacob Epstein and Constantin Brâncuși, also a bit un-dynamic, insipidly faux-modern and backwards-looking. And then, adding the context, knowing about Gill’s religious beliefs, a bit churchy, and then, knowing about his abuse of his daughters, hypocritically pious too; it leaves a bad taste. Which doesn’t stop people from loving it, and nor should it; the art didn’t abuse anyone. (This short article by Waldemar Januszczak is very good on Gill I think).
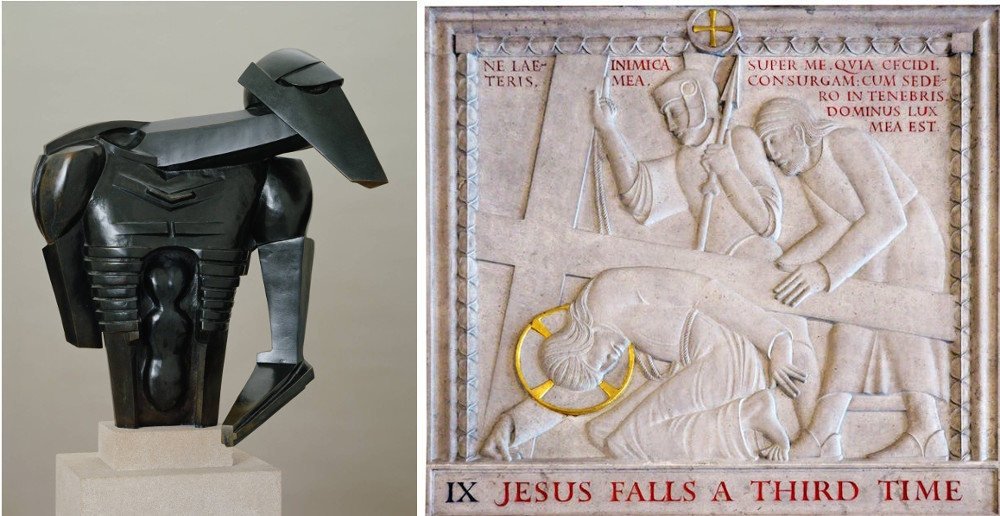

Right: Eric Gill – Stations of the Cross (1913-18)
But one of the points about Gill is that even his apologists probably wouldn’t, these days, hold an exhibition of Gill the artist without at least acknowledging the problems with Gill the man. More my cup of tea, and more relevant to now, the Scottish National Gallery of Modern Art will be hosting an exhibition of Emil Nolde’s work this summer. German Expressionism (or in Nolde’s case, German-Danish Expressionism) is one of the areas of art I love the most and, although Nolde is not one of my favourite artists I will be excited to see his work. But. Emil Nolde was a member of the Nazi Party. That of course doesn’t change his paintings, but it makes them – and the exhibition – problematic for several reasons. The main reason for me, is that, in its pre-exhibition publicity at least, the NGS makes no mention of his Nazism whatsoever. That might still be okay, I suppose, if they didn’t include this little snippet in their bio:
“This exhibition…covers Nolde’s complete career, from his early atmospheric paintings of his homeland right through to the intensely coloured, so-called ‘unpainted paintings’, works done on small pieces of paper during the Third Reich, when Nolde was branded a ‘degenerate’ artist and forbidden to work as an artist.”

There is a certain amount of schadenfreude in this detail. But there is also the ghost of fellow Expressionist Elfriede Lohse-Wächtler, murdered at Sonnenstein castle in 1940 as part of a government programme to eliminate the mentally ill, and of German-Jewish painters like Charlotte Salomon and the surrealist Felix Nussbaum, murdered in Auschwitz in 1943 and 44 respectively. As a member of the Nazi Party (and an enthusiastic one), Nolde was to an extent complicit in their deaths. For Nolde, ‘entartete kunst’, a policy that he didn’t necessarily oppose in general, meant he had to paint unobtrusively, in private and couldn’t exhibit his work until after the war. For those artists it meant a death sentence, for many others it meant harassment or exile. A more wide-ranging exhibition in which Nolde’s paintings bridge the gap between the work of his fellow ‘degenerates’ including perhaps some of Nussman’s Auschwitz paintings, and the art of Nazi-approved painters like Adolf Ziegler or Conrad Hommel would be a strange and indigestible (and chronologically back to front) thing perhaps, but I think that failing that kind of an overview we, at the very least, shouldn’t be encouraged to feel sorry for Nolde that he had to work in secret because of the actions of the government he supported.

Is Nolde’s art then ‘Nazi art’? No, or at least not in the same way that state-sponsored art under Hitler was. It isn’t didactic, realist or heroic. Nolde saw expressionism and therefore his own painting as definitively German, and was deeply moved by colour, which he equated with emotion. The works of his which I like best (which, maybe coincidentally long pre-date even the idea of the Third Reich and belong to the period when he had recently been in contact with the younger artists of Die Brücke) translate that emotion into intense and visionary land- and seascapes. These pictures feel utterly free of the ideology of Nazism – but that said, even under Nazi rule, the German ideal of the nude Freikörperkultur (Free Body Culture) and ‘oneness with nature’ was respectable in a way that was unthinkable in the UK, so the apparent freedom of the painting need not be reflected in the kind

of egalitarian ideals that artists like Ernst Ludwig Kirchner expressed in their art. If expressionism can be seen as the ultimate kind of subjective painting; where the aim is ultimately to make the viewer feel what the artist feels by filtering a subject through the distorting lens of their individual perception, then Nolde’s paintings show the world as it was felt by someone who could write, in 1938;

As to the question of how easy it is to like Nolde’s ‘unpainted pictures’, I’ll have to wait for the exhibition.
How do you solve a problem like Morrissey (it solves itself)
The Nolde exhibition is only one reason that these issues have been on my mind recently; the other, more personal one is Morrissey. Now, Morrissey is clearly not John Wayne Gacy, or Adolf Hitler, or even Emil Nolde. Nor is he, unlike Varg Vikernes, whose music I also like some of, a murderer or actual Nazi. But I never felt let down by any of those people; with Varg I knew about him before I ever heard his music, I have no emotional investment in it, whereas Morrissey’s recent utterances seem completely at odds with the worldview of his earlier music; which is not his problem, or his fault. I simply interpreted what I wanted to from the art he created, just as it’s possible to look at Emil Nolde’s work and see beauty and freedom there, even if that freedom and beauty is diametrically opposed to the views he professed in his non-artistic life.
I first listened to The Smiths and Morrissey when I was 17, although I was aware of them/him years before. Of all the music I loved as a teenager I think Morrissey’s was the music I identified with the most. I loved The Cure and Joy Division and The Fall probably as much, but their music was – I suppose because it’s less lyrically straightforward – less personal to me. To this day, Morrissey’s lyrics (up to the mid 90s at least) are engraved on my memory and I certainly know more of his lyrics by heart than any other band or artist’s. It’s been very clear for a while now (and murkily apparent for much, much longer) what kind of person, politically, Morrissey is. And that’s fair enough; he is entitled to his views, even if I think he’s wrong and don’t feel inclined to fund him any further (I still think he is more complex than his worst detractors would say, but so what?)
It’s not really any use to say as some people do, that there are artists out there making great work who don’t have extreme right wing views. Obviously that’s true; but unless their art speaks to you personally, why would you care? And most of the time, one has no idea what opinions or beliefs of an artist are anyway, unless they specifically say so. To me personally, art that is explicitly political/religious or politically/religiously-motivated rarely connects on a very deep level; and to paraphrase Cyndi again, it’s not real unless I feel it. But I always felt The Smiths’ music, deeply, and much of Morrissey’s solo stuff too, though it is less critically acclaimed. His recent/latest statements in the press just don’t seem like the words of someone who could write “It’s so easy to laugh/It’s so easy to hate/It takes strength to be gentle and kind”, but that’s people for you.
Initially, several controversies ago, I decided that although I wouldn’t actively avoid Morrissey and his works, I would no longer buy them in a way which would financially benefit him; mean and possibly unfair I know, but that’s people for you too. I am not someone who is going to burn records, CDs and books, or even throw/give them away in disgust, if they have ever meant anything to me. But then came the latest and most crass Morrissey interview (so far) and I got to the point where I’d actually be kind of embarrassed to buy anything Morrissey-related at all. It’s not so much (as one example out of many) the factual inaccuracy of statements like “Hitler was left-wing” – people have been saying moronic things like that (Hitler was a Zionist etc etc etc) for many years. It’s the fact that, as with those who claim the death toll in the holocaust has been exaggerated, people like Morrissey seem to think that this amazing revelation is in any way relevant to the things his regime did and how one should feel about it. As with (irony!) people who taunt vegetarians with ‘Hitler was a vegetarian’, it spectacularly misses the point; Hitler is not famous because he’s a vegetarian, any more than he’s famous for his ‘left-wing’ views. And you know that, so don’t be so stupid.
But anyway, in the end my fears that the unhappy soundtrack to my youth/life would be tainted only came half true. When Morrissey songs popped up in a shuffle I found that, without any feeling of revulsion, drama or anguish, I just didn’t want to hear them anymore. The connection seems to be gone, without regret and possibly with the relief that I was never – despite the fact that I even, unrepentantly, like his autobiography – one of those Morrissey obsessives. Maybe one day my love of his music will come back, maybe not. As Cyndi says, it’s not real if you don’t feel it and, right now I just don’t, so it isn’t. Ho hum.







 It’s not National, to my knowledge it’s rarely socialist, but it mostly is black metal; National Socialist Black Metal (hereafter, NSBM) annoys people by being ‘too evil’, or at least evil in the wrong way. As the snuff movie is to the horror movie, it seems, NSBM is to BM. There are a couple of flaws in this analogy; firstly, it suggests that black metal in general is, like horror movies, some kind of fantasy (which it certainly often is, but isn’t necessarily) and secondly, that NSBM isn’t some kind of fantasy (see previous parentheses). The Nazis of World War 2 represent the ‘ultimate evil’ to people of the post-war generations because whereas even the worst serial killers of the 20th century ‘worked’ on an individual, localised scale, the Nazis made murder into an ideology and ultimately an industry. That is, they functioned in ways that are relevant and relate-able to the daily lives and experiences of most people; but in bringing that mundane quality to extermination; ‘death factories’ they ultimately created something more frightening than a lone maniac. So is Nazi black metal the embodiment of that famously banal evil and therefore the ultimate in musical terrorism? Hmm, possibly not but let’s see…
It’s not National, to my knowledge it’s rarely socialist, but it mostly is black metal; National Socialist Black Metal (hereafter, NSBM) annoys people by being ‘too evil’, or at least evil in the wrong way. As the snuff movie is to the horror movie, it seems, NSBM is to BM. There are a couple of flaws in this analogy; firstly, it suggests that black metal in general is, like horror movies, some kind of fantasy (which it certainly often is, but isn’t necessarily) and secondly, that NSBM isn’t some kind of fantasy (see previous parentheses). The Nazis of World War 2 represent the ‘ultimate evil’ to people of the post-war generations because whereas even the worst serial killers of the 20th century ‘worked’ on an individual, localised scale, the Nazis made murder into an ideology and ultimately an industry. That is, they functioned in ways that are relevant and relate-able to the daily lives and experiences of most people; but in bringing that mundane quality to extermination; ‘death factories’ they ultimately created something more frightening than a lone maniac. So is Nazi black metal the embodiment of that famously banal evil and therefore the ultimate in musical terrorism? Hmm, possibly not but let’s see…








