 There is a (completely valid) argument that originality in the arts is overrated; and clearly it is better to have something derivative or traditional that is good, than something completely original that is bad. But at the same time, to take conventional or traditional tools – be they guitars, words or paint & brushes – and to use them to create something new, is a challenge no less difficult – but less heralded – than being a true pioneer.
There is a (completely valid) argument that originality in the arts is overrated; and clearly it is better to have something derivative or traditional that is good, than something completely original that is bad. But at the same time, to take conventional or traditional tools – be they guitars, words or paint & brushes – and to use them to create something new, is a challenge no less difficult – but less heralded – than being a true pioneer.
In the Germany of the early 20th Century, there was a lot to reject – not only centuries of rigid regional – Prussian, Saxon, Bavarian – tradition, but also the more recent social and moral repression of Kaiser Wilhelm’s conservative regime (more or less a militarised version of his British aunt’s “Victorianism”). On top of this, there was, in the art world, the relatively recent absorption of realism and impressionism, radical only a generation before, but already becoming a new kind of academicism a decade later.
When a group of young artists formed a group called Die Brücke (‘The Bridge’), late in the first decade of the century, one of their aims was to strip away the patina of suffocating ‘style’ and orthodox practice that had grown up between subjects or themes and the viewing public. At the same time, they intended to apply this philosophy to their own lives, freeing themselves from formalised German society and its stifling conventions during summer painting trips into the beautiful landscapes of rural Germany.  Despite these radical aims, the artists were not wholly iconoclastic; rather than rejecting all that had gone before, they looked to art with the most primal, emotional impact, from both home and abroad; both the tribal, ‘primitive’ art of non-western cultures, and Germany’s own ‘barbaric’ Gothic past. In terms of this kind of visceral impact, the group’s most successful works are probably those combining those things over which society and its civilising influence had little control; the human body and the natural world it has inhabited since the dawn of humankind. These works retain their impact over a century later, but although (like all truly ‘successful’ visual art) they require no explanation in order to be understood, the story and context of their genesis is fascinating in itself and helps to illuminate the works and their still-poweful impact.
Despite these radical aims, the artists were not wholly iconoclastic; rather than rejecting all that had gone before, they looked to art with the most primal, emotional impact, from both home and abroad; both the tribal, ‘primitive’ art of non-western cultures, and Germany’s own ‘barbaric’ Gothic past. In terms of this kind of visceral impact, the group’s most successful works are probably those combining those things over which society and its civilising influence had little control; the human body and the natural world it has inhabited since the dawn of humankind. These works retain their impact over a century later, but although (like all truly ‘successful’ visual art) they require no explanation in order to be understood, the story and context of their genesis is fascinating in itself and helps to illuminate the works and their still-poweful impact.
Despite the Victorianism mentioned above, there were currents of liberal thought in Wilhelmine Germany that were to influence the art of the Brücke. The artists were of that generation (roughly the same one as Hitler), who were inspired by the writings of the philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche. In Thus Spake Zarathustra (1892), Nietzsche stressed the need to destroy the sterile values of decadent civilisation, and cast off history in order to create a positive, healthy art. In 1906’s posthumous The Will To Power, he stressed the point even more clearly – ‘The savage… is a return to nature – and in a certain sense his recovery, his cure from culture.’ This was to prove an inspirational doctrine to young artists, who were to find an escape from the stifling pressure of the stagnant past (and present) in the so-called ‘primitive’ art of non-western cultures. At the same time, the cult of nature was widespread and very respectable throughout Germany in this period and was manifested in groups such as the Wandervögel, which was devoted to exploring the German countryside, as well as in health and nudist groups which had grown up partly as a revolt against the effects of rapid industrialisation. 
Although the aspect of nudity seems, even in the 21st century, a symptom of liberalisation, in fact this was an element of the zeitgeist that influenced a whole generation regardless of its political beliefs; both the Communist and Nazi parties in Germany were involved in boy scout style activities with a naturist focus, and even at its height the Third Reich celebrated, rather than suppressed, nude (non-sexual) group activities, and the Hitler Youth had a strong outdoors element. Interestingly, one of the most important authors in this respect was not Nietzche but Jack London, with his stirring tales of (to be honest, fully clothed) adventures in the wilderness of America, such as The Call of the Wild and White Fang.

Although avowedly modern, the Brücke did not have a straightforward view of the recently industrialised, unified Germany. Until 1871 Germany consisted of twenty-five individual states, and regional identity – artistic as well as political – remained strong. This meant that Kaiser Wilhelm’s regime indulged in the kind of extreme nationalist propaganda later carried even further by the Nazi Party, using a semi-mythical German past to appeal to national, rather than local, feelings of patriotism. As in the UK, the speed with which the country became industrialised led to a nostalgic yearning for the rural past, in Germany defined by reference to the ‘Fatherland’ and the volk of Germany, whose traditional way of life was perceived by conservative observers to be threatened by the influx of foreign workers necessary to keep the country’s industrial heart beating. Nationalistic feeling was not however, only the preserve of the political right; one of the aims of Brücke founder member Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, even before the group came together, was ‘the renewal of German art’, although, unlike the statements of Joseph Goebbels and his ilk, this did not imply any denigration of non-German art. This reinforces the fact that, despite surface similarities, the work of The Brücke was entirely in opposition to the Romantic right-wing sentiments then emerging.
The Brücke, consisting of Fritz Bleyl, Erich Heckel, M ax Pechstein, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl
ax Pechstein, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl
Schmidt-Rottluff and Emil Nolde among others, made excursions to the Moritzburg lakes outside of Dresden, and paintings like Pechstein’s Open Air (Moritzburg) (1910) and Erich Heckel’s series of Bathers attempt to express the communal freedom from convention which was one of the group’s main aims. In these pictures, the bold compositions and the use of vivid colour links the bathers to the landscape they inhabit, with flesh tones reflected in the colours of the trees and land. The two-dimensional quality of the paintings also integrates the figures within the landscape, giving a strong sense of surface deign, enhanced by the simplification of both figures and objects, all generalised to basic shapes and painted in intense saturated colour. The ‘primitive’, almost crude aspect of these paintings could itself be read as a straightforward criticism or rejection of modern urban society and its values, but the real situation was far more complex.
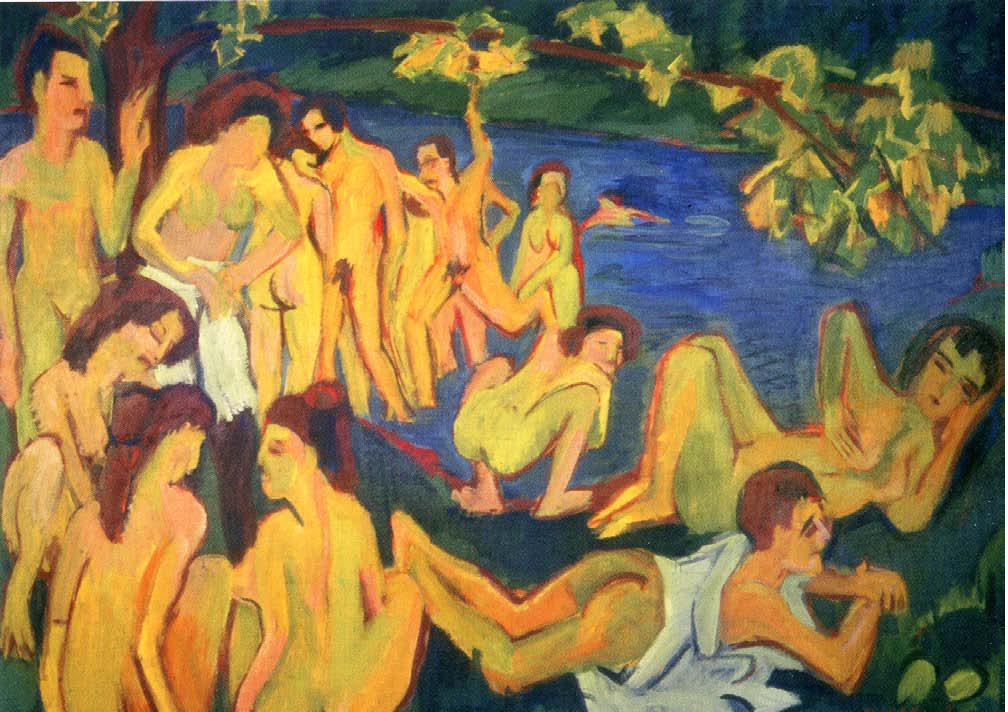 Shortly after their founding in 1905, the Brücke issued a manifesto which stressed their desire to rebel against the ‘long established older forces’ at work in Germany and their commitment to modernity. What they didn’t mean was modernity as embodied in the Berlin Secession, then only seven or eight years old; a modernist movement (in some ways comparable to, although more formalised than, the Bloomsbury group in the UK) based on the belated acceptance of Impressionism in German art. German Impressionist Max Liebermann and his followers effectively sowed the seeds of their own destruction by exhibiting the works of artists far more advanced in modernism than themselves, including Munch, Van Gogh, Cezanne and the Fauves, inadvertently highlighting the inoffensive, pleasant mildness of their own work.For the Brücke artists however, it was the expressiveness of Munch and Van Gogh, and the Fauves’ intense use of colour that were to point the way forward.
Shortly after their founding in 1905, the Brücke issued a manifesto which stressed their desire to rebel against the ‘long established older forces’ at work in Germany and their commitment to modernity. What they didn’t mean was modernity as embodied in the Berlin Secession, then only seven or eight years old; a modernist movement (in some ways comparable to, although more formalised than, the Bloomsbury group in the UK) based on the belated acceptance of Impressionism in German art. German Impressionist Max Liebermann and his followers effectively sowed the seeds of their own destruction by exhibiting the works of artists far more advanced in modernism than themselves, including Munch, Van Gogh, Cezanne and the Fauves, inadvertently highlighting the inoffensive, pleasant mildness of their own work.For the Brücke artists however, it was the expressiveness of Munch and Van Gogh, and the Fauves’ intense use of colour that were to point the way forward.
 Perhaps not surprisingly, given the sense of design and structure in their works, the four founders of the Brücke; Fritz Bleyl, Erich Heckel, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl Schmidt-Rottluff were architecture students with little or no training in painting. Being based in Dresden was important, as it not only gave them access to some of Germany’s most unspoiled countryside, but also the opportunity to study modern European painting (Van Gogh’s art was exhibited in the city as early as 1903) alongside the then-neglected mediaeval and Renaissance German art.
Perhaps not surprisingly, given the sense of design and structure in their works, the four founders of the Brücke; Fritz Bleyl, Erich Heckel, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl Schmidt-Rottluff were architecture students with little or no training in painting. Being based in Dresden was important, as it not only gave them access to some of Germany’s most unspoiled countryside, but also the opportunity to study modern European painting (Van Gogh’s art was exhibited in the city as early as 1903) alongside the then-neglected mediaeval and Renaissance German art.
Van Gogh set a powerful example of how to imbue not only figures, but also landscape with personal, symbolic and emotional meaning, with colour used in an expressive rather than realistic way. At the same time, the Dresden Ethnographic Museum displayed many ‘primitive’ works from the South Seas and elsewhere. Particularly important for the group were some roof beams from the Palau islands in the South Seas, which had been taken by Germany as part of the Kaiser’s aggressive policy of Imperial expansion. While these influences were important for the group, it’s probably fair to say they helped liberate it from contemporary restrictions, rather than actually shaping the art that they produced.
 A case in point is Kirchner’s paintings from the group’s summer excursions, such as Bathers at Moritzburg and Three Nudes in A Forest (1909). These are not exercises in emulating primitive art and neither are they intended as purely decorative works, but instead they attempt to recreate the sense of freedom that the artist and his friends actually experienced at the time, without reference to the accepted conventions of nude or landscape painting. While fascinated by the art of tribal, non-European cultures, the Brücke artists were ignorant of its context and meaning, but this actually strengthened, rather than undermined its usefulness to the group. ‘Primitive’ art was resonant mainly for its position outside of the Western European art tradition; whether it was truly ‘untutored’ (unlikely) or sprang from cultures who were more in touch with the basic instincts and impulses obscured by centuries of religion and convention (questionable), this was the perception of the westerners encountering it for the first time. This meant that its features, such as the simplification and generalisation of the human figure and the lack of mathematical perspective were potent tools for artists trying to make art based on primal feeling rather than convention.
A case in point is Kirchner’s paintings from the group’s summer excursions, such as Bathers at Moritzburg and Three Nudes in A Forest (1909). These are not exercises in emulating primitive art and neither are they intended as purely decorative works, but instead they attempt to recreate the sense of freedom that the artist and his friends actually experienced at the time, without reference to the accepted conventions of nude or landscape painting. While fascinated by the art of tribal, non-European cultures, the Brücke artists were ignorant of its context and meaning, but this actually strengthened, rather than undermined its usefulness to the group. ‘Primitive’ art was resonant mainly for its position outside of the Western European art tradition; whether it was truly ‘untutored’ (unlikely) or sprang from cultures who were more in touch with the basic instincts and impulses obscured by centuries of religion and convention (questionable), this was the perception of the westerners encountering it for the first time. This meant that its features, such as the simplification and generalisation of the human figure and the lack of mathematical perspective were potent tools for artists trying to make art based on primal feeling rather than convention.
To tap into the desired raw creativity, the artists valued informality and impulsiveness, training themselves to capture the human figure as economically as possible by employing amateur models and having them pose for nude studies for a maximum of fifteen minutes per sitting. The nudes of Kirchner’s paintings owe as much to these studies as to any ‘primitive’ prototypes. Similarly, although there are parallels between the Brücke’s use of flat intense colour and that of the Fauves, an equally (or more) valid comparison is with the simplified use of colour created by woodblock printing, a major activity of the group from its inception onwards. Whereas the Fauves used colour boldly, but for harmonious and decorative purposes, the Brücke used it to reinforce the sense of vigour and life within the group’s dynamic compositions as well as for symbolic impact.
 As previously mentioned, nudity in itself was not controversial in Germany; not only were liberal and conservative alike agreed on the healthiness of nudism and outdoor pursuits (an aspect of German society that would become even more dominant in the inter-war Weimar period and beyond),
As previously mentioned, nudity in itself was not controversial in Germany; not only were liberal and conservative alike agreed on the healthiness of nudism and outdoor pursuits (an aspect of German society that would become even more dominant in the inter-war Weimar period and beyond),
but the academic tradition of German painting too, celebrated the nude in its romantic, Arcadian visions. The Brücke’s attitude to nudity is, however, possibly the most revolutionary aspect of their work. The teaching of art has usually stressed (and in general still does) the human figure as form rather than gender and structure rather than meaning.
The Fauves (notably in works like Matisse’s Joie de Vivre (1906) or The Dance (1909)) aimed at a  satisfying decorative composition and a sense of harmony and peace, but the Brücke artists – and Kirchner in particular – imbued their figures with a positive and sexual energy, influenced as much by the writings of Nietzsche and Walt Whitman as by any artistic source. In this, they were influenced to an extent by Munch, but whereas the Norwegian’s haunting and bleak paintings expressed his anxieties about sex and relationships, the Brücke used the depiction of nudity to purge their work of the sexual repression and neuroses that was the darker side of Wilhelmine Germany’s obsession with nudity and hygiene. Two paintings by Kirchner highlight the importance the setting has in the meaning at atmosphere of the group’s treatment of the body.
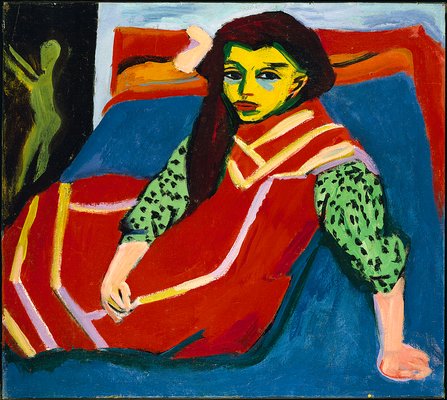
satisfying decorative composition and a sense of harmony and peace, but the Brücke artists – and Kirchner in particular – imbued their figures with a positive and sexual energy, influenced as much by the writings of Nietzsche and Walt Whitman as by any artistic source. In this, they were influenced to an extent by Munch, but whereas the Norwegian’s haunting and bleak paintings expressed his anxieties about sex and relationships, the Brücke used the depiction of nudity to purge their work of the sexual repression and neuroses that was the darker side of Wilhelmine Germany’s obsession with nudity and hygiene. Two paintings by Kirchner highlight the importance the setting has in the meaning at atmosphere of the group’s treatment of the body.  Girl With A Cat – Franzi (1910) is an ambiguous image; the modern interior and the ribbons in Franzi’s hair, combined with the viewpoint which forces the viewer to look down on the girl, creates an uneasy sense of vulnerability and tension, which, despite the painting’s vibrant col
Girl With A Cat – Franzi (1910) is an ambiguous image; the modern interior and the ribbons in Franzi’s hair, combined with the viewpoint which forces the viewer to look down on the girl, creates an uneasy sense of vulnerability and tension, which, despite the painting’s vibrant col our, makes it comparable in effect to Munch’s Puberty (1895). By removing the same model from an urban environment in Franzi With a Bow and Arrow (1909-11) the tension is replaced instead by a vibrant and carefree energy. The natural setting and dynamic pose (very much a standard image of German nudism) neutralise the troubled psychological aspects apparent in the urban setting.
our, makes it comparable in effect to Munch’s Puberty (1895). By removing the same model from an urban environment in Franzi With a Bow and Arrow (1909-11) the tension is replaced instead by a vibrant and carefree energy. The natural setting and dynamic pose (very much a standard image of German nudism) neutralise the troubled psychological aspects apparent in the urban setting.

On the surface, this transformation would seem simply to conform to the spiritual regeneration of Germany as Heimat (homeland) as espoused by right-wing nudist groups with their obsession with cleanliness and sports, but in fact it is far more revolutionary. The carefree sexuality seen in a painting like Kirchner’s Striding Into the Sea (completed in 1912) was definitely not approved of by Kaiser Wilhelm’s establishment, and goes beyond the somewhat detached approach to the nude in contemporary French art.  The Brücke were in a sense living (or at least trying to live) their philosophy; on their summer trips the group went beyond the regimented nudist groups to stay in secluded woodland spots where they could bathe alongside their female models in what Max Pechstein described as ‘perfect harmony’; just as in their paintings (of course this has its own troubling aspect, since the group was mostly male and the girls involved were, in some cases, paid to be there). There is in fact a noticeable change in tone in the group’s work after 1911 when they moved to Berlin, where Kirchner’s nude paintings tend to separate into urban studies of sexuality as the summer trips ended and they instead began to go on trips individually, with, not surprisingly, far less communal or social feeling in the paintings they completed there.
The Brücke were in a sense living (or at least trying to live) their philosophy; on their summer trips the group went beyond the regimented nudist groups to stay in secluded woodland spots where they could bathe alongside their female models in what Max Pechstein described as ‘perfect harmony’; just as in their paintings (of course this has its own troubling aspect, since the group was mostly male and the girls involved were, in some cases, paid to be there). There is in fact a noticeable change in tone in the group’s work after 1911 when they moved to Berlin, where Kirchner’s nude paintings tend to separate into urban studies of sexuality as the summer trips ended and they instead began to go on trips individually, with, not surprisingly, far less communal or social feeling in the paintings they completed there.
The idyllic nature of the Brücke’s Moritzburg paintings, does not, however, mean that the artists made the standard distinction between a healthy outdoor life and a decadent urban one. Many of the group’s images of the city, especially those painted before the relocation to Berlin, explore their sense of excitement they felt on the fringes of urban modern life, rather than a Munch-like sense of alienation. Also, whereas the Moritzburg paintings were essentially attempts to capture the mood and a philosophy of an enclosed, self-created world, their urban paintings were more self-consciously artistic; whereas German academic painting (like most 19th century academic painting) was essentially an amalgam of romanticism and the mathematical principles and idealising tendencies of the Italian renaissance, a painting like Kirchner’s Standing Nude With A Hat (1910) looks to the then neglected German ‘primitives’ such as Lucas Cranach the Elder, whose Venus and Cupid, like Kirchner’s nude, is almost certainly the portrait of a real court lady, her fashionable hat stressing the flimsiness of the mythical setting.
Following the move to Berlin, the Brücke became less close-knit as a group and the influence of art as opposed to lifestyle on their painting became more direct. The theme of the nude in nature remained important, but the works became less unified as Kirchner and Erich Heckel began to travel to the Baltic island of Fehmarn, while Max Pechstein painted at Nidden and Karl Schmidt-Rottluff visited  Dangast, by the North Sea. Newer member Otto Müller, who joined the Brücke in 1910 had impressed his fellow artists with the woodcut-like flatness of his painting style and his paintings, such as Bathers (c.1912) and Reclining Nude in Dunes (c.1915) are far less dramatic and strident than the group’s earlier works, but reflect a similar interest in non-European (and especially ancient Egyptian) painting.
Dangast, by the North Sea. Newer member Otto Müller, who joined the Brücke in 1910 had impressed his fellow artists with the woodcut-like flatness of his painting style and his paintings, such as Bathers (c.1912) and Reclining Nude in Dunes (c.1915) are far less dramatic and strident than the group’s earlier works, but reflect a similar interest in non-European (and especially ancient Egyptian) painting.
Müller’s main interest was in simplicity and clarity and to this end he began to use distemper to gain a matt, two-dimensional effect. Despite its relatively conventional aspects, Müller’s delicate art was to influence Kirchner’s own painting.
In Fehmarn, Kirchner felt, like Gauguin in Tahiti, that he had found a place unspoiled by modern industrial society, but in reality it was this society (in Kirchner’s case the recently-built railway network) that made these trips possible. In works such as Five Bathers at the Lake (1911) and Two Bathers, Fehmarn (1913) Kirchner’s painting has become more tightly controlled than before, and the figures are based on ‘primitive’ sources, rather than simply being depicted with primitive energy. Even more than Kirchner’s had, Müller’s work shows the influence of the forms of African sculpture (and of Kirchner’s carved driftwood figures), rather than simply using them as models of simplicity and freedom from Western art conventions.
 In this period Kirchner himself was influenced by John Griffiths’ book Paintings in the Buddhist Cave Temples of Ajanta (1896) and by comparison with the Moritzburg works, these paintings are calmer, more decorative and stylized and, crucially, feature no male figures; this is not an artist recording a world in which he plays an integral part, but is instead depicting and celebrating something which is ‘exotic’ and separate from the artist’s everyday experience; in fact a ‘primitive’ record, like Gauguin and Bernard’s depiction of rustic life in Pont Aven; not a new art for a new society.
In this period Kirchner himself was influenced by John Griffiths’ book Paintings in the Buddhist Cave Temples of Ajanta (1896) and by comparison with the Moritzburg works, these paintings are calmer, more decorative and stylized and, crucially, feature no male figures; this is not an artist recording a world in which he plays an integral part, but is instead depicting and celebrating something which is ‘exotic’ and separate from the artist’s everyday experience; in fact a ‘primitive’ record, like Gauguin and Bernard’s depiction of rustic life in Pont Aven; not a new art for a new society.
 Gauguin was also an important influence on the works Karl Schmidt-Rottluff painted at Nidden, (Nidden being its German name; properly Nida, on the Lithuanian coast) in 1913. Pictures like Nudes in the Dunes and Three Nudes retain the intense saturated colour that marked the Brücke’s early style, and Schmidt-Rottluff also integrates figures and landscape more completely than Kirchner did in this period. The hot, complementary colours are clearly Fauve-influenced, and like Kirchner and Müller, the artist attempts to create images that are flat and decorative, rather than realistic or three-dimensional.
Gauguin was also an important influence on the works Karl Schmidt-Rottluff painted at Nidden, (Nidden being its German name; properly Nida, on the Lithuanian coast) in 1913. Pictures like Nudes in the Dunes and Three Nudes retain the intense saturated colour that marked the Brücke’s early style, and Schmidt-Rottluff also integrates figures and landscape more completely than Kirchner did in this period. The hot, complementary colours are clearly Fauve-influenced, and like Kirchner and Müller, the artist attempts to create images that are flat and decorative, rather than realistic or three-dimensional.
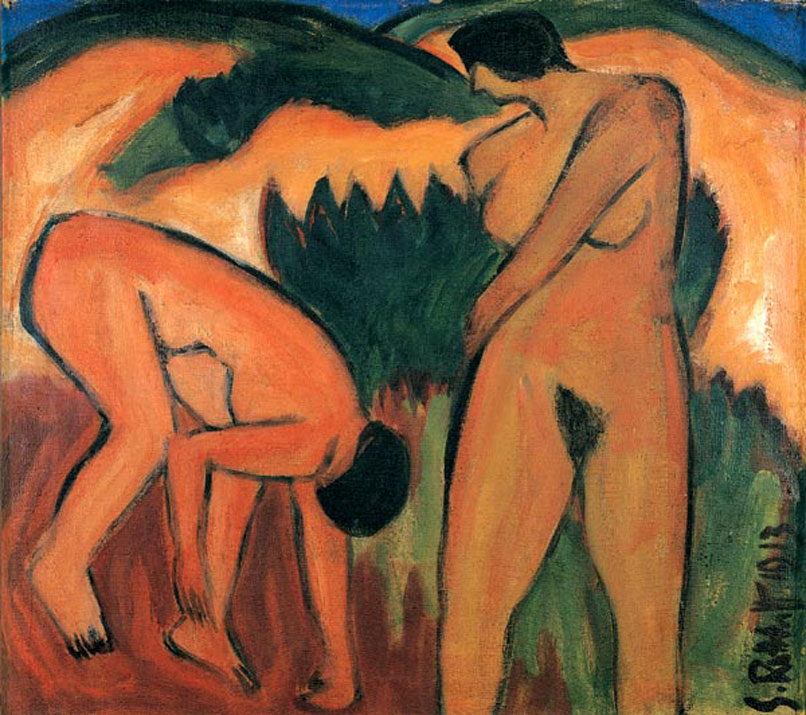 Schmidt-Rottluff ensured that there was little background/foreground or distancing effects by making horizon lines either high or non-existent and eliminating empty space from his pictures. At the same time, this, while definitively modern by the standards of its time, is idyllic and escapist, rather than rebellious or reforming in intent. Schmidt-Rottluff and Erich Heckel experimented with the cubist style then emerging in France, but it was a short-lived phase for Schmidt-Rottluff. Heckel was more serious, becoming friendly with the members of the Expressionist group Der Blauer Reiter, whose works were indebted to both Cubism and Futurism. He was also influenced by William Worringer’s 1908 book Abstraction and Empathy, which argued that the artist could only
Schmidt-Rottluff ensured that there was little background/foreground or distancing effects by making horizon lines either high or non-existent and eliminating empty space from his pictures. At the same time, this, while definitively modern by the standards of its time, is idyllic and escapist, rather than rebellious or reforming in intent. Schmidt-Rottluff and Erich Heckel experimented with the cubist style then emerging in France, but it was a short-lived phase for Schmidt-Rottluff. Heckel was more serious, becoming friendly with the members of the Expressionist group Der Blauer Reiter, whose works were indebted to both Cubism and Futurism. He was also influenced by William Worringer’s 1908 book Abstraction and Empathy, which argued that the artist could only  escape the confusion of the chaotic modern world by depicting nature in a way which simplified the organic forms of nature into something abstract, crystalline and ‘imperishable’. Heckel’s 1913 painting Glassy Day shows the influence of this doctrine in its simplified, dynamic forms. The figure is generalised in the manner of the African sculpture the group had seen, but though there is the influence of the dynamic lines of Futurism, the jagged reflections do not disturb the calmness of the scene, but instead suggest an intense clarity of light and atmosphere. Again though, Glassy Day seems to represent escape, rather than rebellion.
escape the confusion of the chaotic modern world by depicting nature in a way which simplified the organic forms of nature into something abstract, crystalline and ‘imperishable’. Heckel’s 1913 painting Glassy Day shows the influence of this doctrine in its simplified, dynamic forms. The figure is generalised in the manner of the African sculpture the group had seen, but though there is the influence of the dynamic lines of Futurism, the jagged reflections do not disturb the calmness of the scene, but instead suggest an intense clarity of light and atmosphere. Again though, Glassy Day seems to represent escape, rather than rebellion.

When the Brücke disintegrated in 1913, it had achieved some of its aims; notably the renewal of a kind of German art which acknowledged developments elsewhere without abandoning the Germanic past. The aim to establish a new and harmonious way of living, outside of the constraints of society had worked for a while, in the kind of artistic commune dreamed of by Van Gogh and Gauguin, but it was ultimately doomed to failure, perhaps because carefree harmony as a way of life robbed the artists’ ambition of any sense of urgency. Even had the group remained true to this aim, it was unlikely to have survived the World War that was almost upon them.
As the Brücke dissolved as a group, the artists went on to pursue their own personal visions, but from this point onwards they were to look at the landscape and the human figure in a detached way, as artists and intellectuals, and not as social revolutionaries; a shame perhaps, but their early work was to stand as a testament to their liberating, life-affirming ideals throughout the Nazi period (when it was, typically, classified as ‘degenerate’ by the authorities) and the freedom they created and recorded still retains its power today.









 Heartbreakingly sad but also funny and rebellious blues performance by one of my favourite blues singers, with brilliant guitar playing by Tampa Red
Heartbreakingly sad but also funny and rebellious blues performance by one of my favourite blues singers, with brilliant guitar playing by Tampa Red






 ax Pechstein, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl
ax Pechstein, Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Karl





 our, makes it comparable in effect to Munch’s Puberty (1895). By removing the same model from an urban environment in Franzi With a Bow and Arrow (1909-11) the tension is replaced instead by a vibrant and carefree energy. The natural setting and dynamic pose (very much a standard image of German nudism) neutralise the troubled psychological aspects apparent in the urban setting.
our, makes it comparable in effect to Munch’s Puberty (1895). By removing the same model from an urban environment in Franzi With a Bow and Arrow (1909-11) the tension is replaced instead by a vibrant and carefree energy. The natural setting and dynamic pose (very much a standard image of German nudism) neutralise the troubled psychological aspects apparent in the urban setting.











