A few years ago a friend sent me a photograph of the ten-year-old us in our Primary School football team. I was able, without too much thought, to put names to all eleven of the boys, but the biggest surprise was that my initial reaction – for maybe a second but more like two seconds – was not to recognise myself. In my defence, I don’t have any other pictures of me at that age, and even more unusually, in that picture I’m genuinely smiling. Usually I froze whenever a camera was pointed at me (and I still do, if it takes too long), but I must have felt safer than usual in a group shot, because it is a real smile and not the standard grimace that normally happened when I was asked to smile for photographs.
I could possibly also be forgiven for my confusion, because in contrast with my present self, ten year old me had no eyebrows, a hot-pink-to-puce complexion and unmanageably thick, wavy, fair hair; but even so, that was the face I looked at in the mirror every day for years and, more to the point, that gangly child with comically giant hands actually is me; but what would I know?

In a recent documentary, the great artist David Hockney made a remark (paraphrased because I don’t have it to refer to) that resonated with me; your face isn’t for you, it’s for other people. As you’d expect of someone who has spent a significant part of his long career closely scrutinizing people and painting portraits of them, he has a point. Everyone around you has a more accurate and certainly more objective idea of what you look like than you do. Even when you see someone ‘in real life’ who you are used to seeing in photographs or films, there’s a moment of mental recalibration; they may look like their image, but the human being before you in three dimensions is on a whole different scale and proportion from the thing you are used to seeing.
I remember reading in some kids’ novel that the young footballer me from that photograph liked (I’m guessing it was by Willard Price but can’t swear to it) that when being shown photographs of themselves, the indigenous people of (I think) New Guinea, not only weren’t impressed, but didn’t recognise them as anything in particular other than little squares of paper. Like Hockney, they had a point; if the Victorian people who invented photography hadn’t grown up with a tradition of ‘realistic,’ representational art would they have seen any relationship between themselves as living, breathing, colourful, space-filling three-dimensional organisms and the monochromatic marks on little flat pieces of paper? The response of the fictional New Guinea tribespeople is far more logical than the expected response (surprise, wonder, awe) in the novel.
Hockney went on further to say that portrait painting (if the sitter is present with the artist) gives a better idea of a person than photography does. At first this is a harder argument to buy into, but it has its own logic too. A photograph, as he pointed out, is a two-dimensional record of one second in time, whereas the portrait painter creates their similarly two-dimensional image from spending time in the company of the sitter and focusing on them – a different, deeper kind of focus, since it engages the brain as well as the senses, than the technical one that happens with a lens, light and film or digital imaging software. A camera doesn’t care what you are like, it just sees how you look, from that angle, for that second. Maybe my big 10-year-old smile really is representative of how I was, but from memory it doesn’t represent that period for me at all.
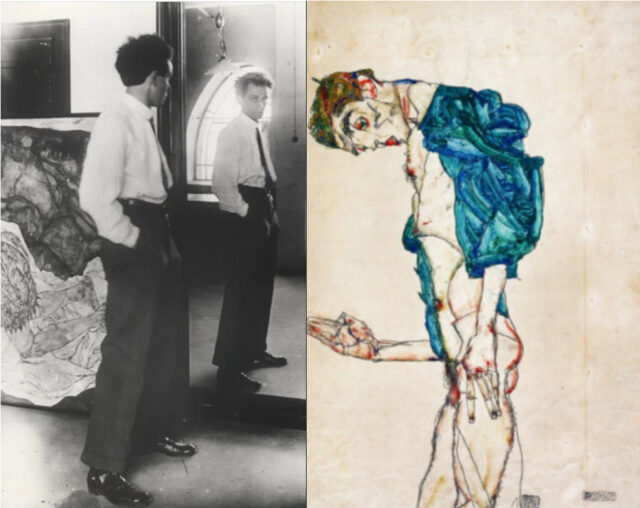
I might never have written this had I not been reading Frank Whitford’s excellent monograph on the Austrian expressionist painter Egon Schiele (Thames & Hudson, 1981). Schiele is famous for (among other things) his twisted, emaciated and fanatically awkward self-portraits. The man he depicts is scrawny, elongated, intense, sometimes almost feline and utterly modern. Schiele in photographs, on the other hand, is quite a different presence. Sometimes he has the expected haunted look and often he has the familiar shock of hair. He sometimes poses almost as awkwardly too, but otherwise he looks surprisingly dapper, civilised, diminutive, square faced and elfin. But if we think – and it seems logical that we do – that the photographs show us the ‘real’ Schiele, then the descriptions of those who actually knew him suggest otherwise.
“a slim young man of more than average height… Pale but not sickly, thin in the face, large dark eyes and full longish dark brown hair which stood out in all directions. His manner was a little shy, a little timid and a little self-confident. He did not say much, but when spoken to his face always lit up with the glimmer of a quiet smile.” (Heinrich Benesch, quoted in Whitford, p.66) This description doesn’t exactly clash with the Schiele of the photographs (though he never appears especially tall), but it’s somehow far easier to identify with the dark-eyed, paradoxically shy and confident Schiele of the self portraits. In his own writings, Schiele seems as tortured and intense as in his paintings, but in photographs he appears confident, knowing and slightly arch. His face, as Hockney says, may not have been for him, but he seems to have captured it in his art in ways that his friends and acquaintances recognised, and which the camera apparently didn’t.

So does that prove Hockney both right (portraiture is superior to photography) and wrong (Schiele did know his own face)? And anyway, what does that have to do with the 10-year old me? Nothing really, except that the camera, objective and disinterested, captured an aspect of me in that second which may or may not have been “true.” Objectivity and disinterestedness are positive qualities for evaluating facts, but when it comes to human beings, facts and truth have a complicated relationship. Photography, through its “realness,” has issues capturing complexities, unless the photographer is aware of them and – Diane Arbus and Nan Goldin spring to mind – has the ability to imbue their work with more than just the obvious surface information that is the camera’s speciality. But (hu)manually-created art, with its human heart and brain directing, naturally takes the relationship between truth and facts in its stride.
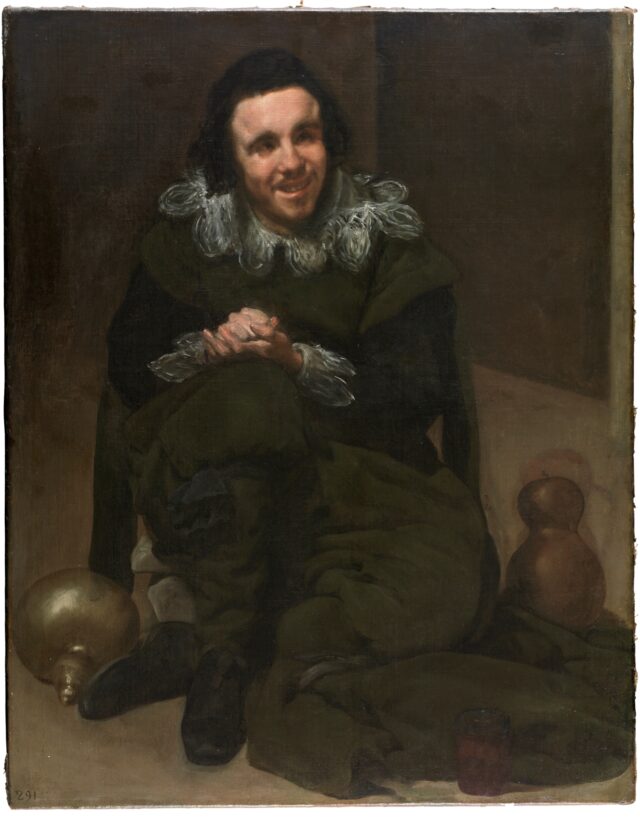
One final example that proves nothing really, except to my satisfaction. Around the year 1635, the Spanish painter Diego Velázquez was tasked with painting portraits of the assorted fools, jesters, dwarfs and buffoons whose lives were spent entertaining the Spanish court. Most of these people suffered from mental or physical disabilities (or both) and were prized (I think that’s a more accurate word than ‘valued’ in this context) for their difference from ‘normal’ people; treated in and viewed as the same way as carnival “freaks” up to the early 20th century in fact.
These people were comparatively privileged – that is, compared to what their lives as someone with a disability would have been like had they not been adopted by the Royal court. But their position in the household was more akin to pets than friends or even servants. Juan de Calabazas (“John of Gourds; a gourd was a traditional jester’s attribute) suffered from unknown mental illnesses and physical tics. In a time and place where formality and manners were rigidly maintained, especially around the monarch – where a misstep in etiquette could have serious or even fatal consequences, buffoons like Juan entertained the court with unfettered, sometimes nonsensical or outrageous speech, impulsive laughter and strange, free behaviour.
In normal 16th-17th century society these people would be lucky even to survive, but in the Court their behaviour was celebrated and encouraged. Velázquez is rightly famous for the empathy and humanity with which he painted portraits of these marginalised figures, but although, as Wikipedia (why not?) puts it; “Velázquez painted [Juan] in a relatively calm state, further showing Velazquez’s equal show of dignity to all, whether king or jester” that seems an unusual response to the portrait below, It’s not untrue, but for me at least, Velázquez’s process of humanisation is painful too. The knowledge that this man lived his life as a plaything of the rich and powerful, alive only because they found him funny is troubling enough. But that pathos seems to be embodied in the picture and you know, or it feels like you know, that Velázquez didn’t find him funny, or at least not only funny. It’s something like watching David Lynch’s The Elephant Man compared to looking at the Victorian photographs of the real Joseph Merrick. Seeing the photographs is troubling, seeing Lynch’s cinematic portrait is too, but it’s deeply moving as well.

All of which may just be a way of saying that a camera is a machine and does what it does – recording the exterior of what it’s pointed at – perfectly, while a human being does, and feels, many things simultaneously, probably not perfectly. Well I’m sure we all knew that anyway. I eventually got eyebrows, by the way.
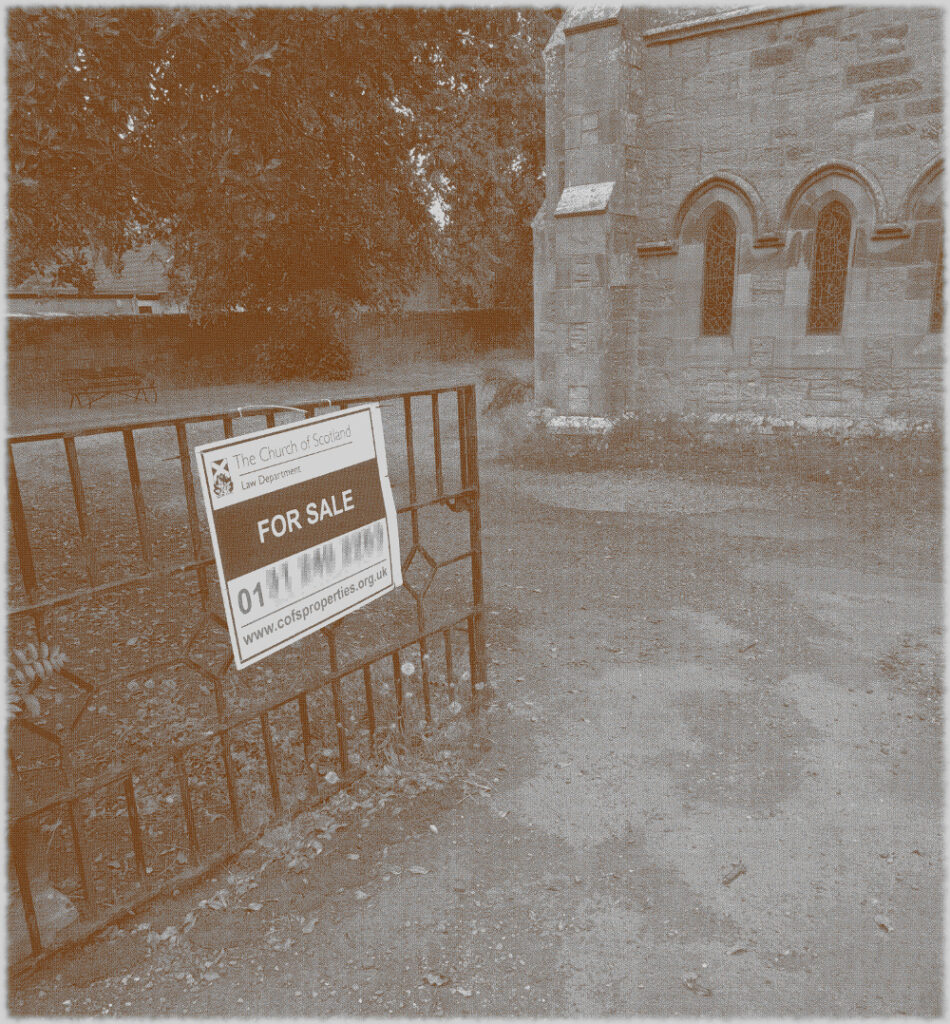
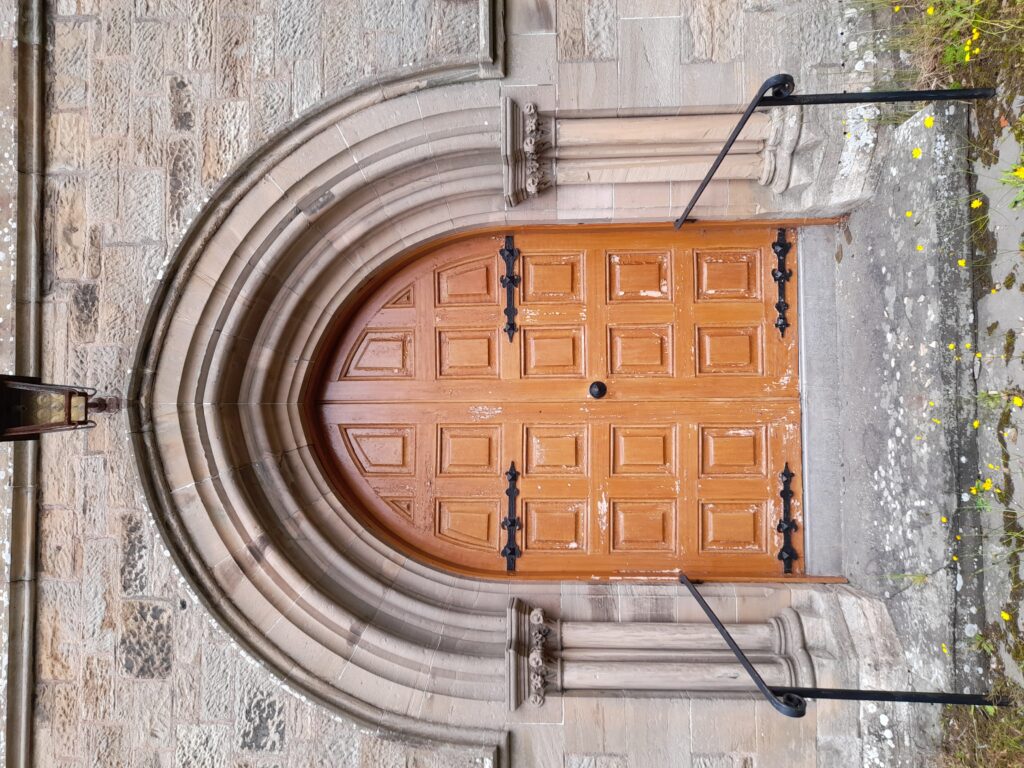
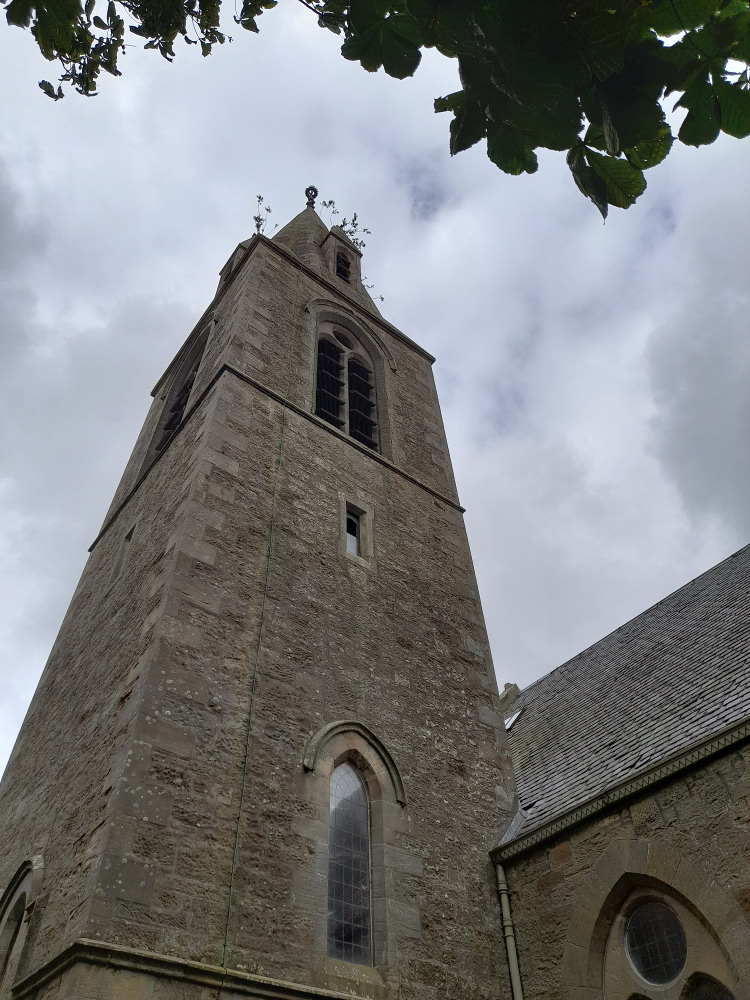







 The idea that money is more important to the Church of Scotland than the buildings that were at the centre of the spiritual and social lives of generations of people (and also, the place that God lived, I guess) seems grotesque, but there it is. It’s just bricks (or stone) and mortar, after all; or that, presumably is the logic, because God doesn’t actually live in a stone building but in either heaven or the hearts of believers etc, etc. And yet, if it’s just a building, how come people can only vandalise houses or schools or barns, but they can “desecrate” churches? “De-consecration” – what the church does in order to render its buildings saleable – is just a non-inflammatory way of saying desecration. De-consecrating the church doesn’t affect the material of the building, but it does remove its purpose – but what it can’t do is remove its history. So if you buy a church, what is it that are you actually buying? In a book I liked as a teenager, Terry Brooks’s Magic Kingdom For Sale – Sold! (1986), a depressed lawyer called Ben Holiday buys what turns out to be something like Narnia or Middle Earth, from a catalogue (nowadays it would be from a website). If Mr Holiday bought a church, he wouldn’t be mystically transported to an otherworldly realm, but he would – and the buyers of these buildings do – become the owner of a place where thousands of people were, in a meaningful way, transported to a place where, whatever the privations and terrors of their daily lives might be, things made some sort of black-and-white sense. Somewhere that virtue was rewarded with eternal paradise, vice was punished with eternal damnation and the person in the pulpit had the correct answers to whatever questions life was throwing at you. You don’t have to believe in any of that to realise that it was (and to some extent I suppose still is) important.
The idea that money is more important to the Church of Scotland than the buildings that were at the centre of the spiritual and social lives of generations of people (and also, the place that God lived, I guess) seems grotesque, but there it is. It’s just bricks (or stone) and mortar, after all; or that, presumably is the logic, because God doesn’t actually live in a stone building but in either heaven or the hearts of believers etc, etc. And yet, if it’s just a building, how come people can only vandalise houses or schools or barns, but they can “desecrate” churches? “De-consecration” – what the church does in order to render its buildings saleable – is just a non-inflammatory way of saying desecration. De-consecrating the church doesn’t affect the material of the building, but it does remove its purpose – but what it can’t do is remove its history. So if you buy a church, what is it that are you actually buying? In a book I liked as a teenager, Terry Brooks’s Magic Kingdom For Sale – Sold! (1986), a depressed lawyer called Ben Holiday buys what turns out to be something like Narnia or Middle Earth, from a catalogue (nowadays it would be from a website). If Mr Holiday bought a church, he wouldn’t be mystically transported to an otherworldly realm, but he would – and the buyers of these buildings do – become the owner of a place where thousands of people were, in a meaningful way, transported to a place where, whatever the privations and terrors of their daily lives might be, things made some sort of black-and-white sense. Somewhere that virtue was rewarded with eternal paradise, vice was punished with eternal damnation and the person in the pulpit had the correct answers to whatever questions life was throwing at you. You don’t have to believe in any of that to realise that it was (and to some extent I suppose still is) important.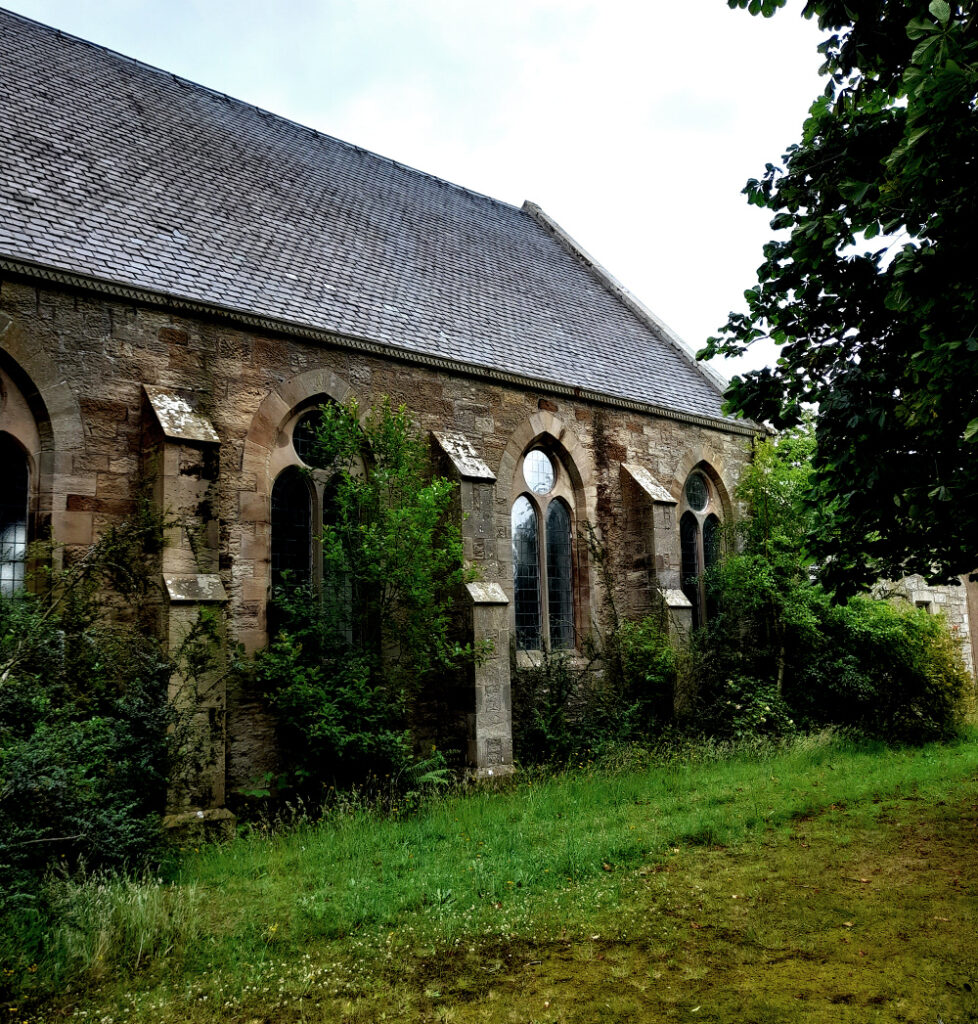 Like, I’m sure, many convinced lifelong atheists (and I’m a very un-spiritual one at that), I love churches. The architecture, the fixtures and fittings, the solemn atmosphere. The idea of building on top of (Native American) Indian burial grounds was enough to fuel horror fiction and urban legend for a century; will turning churches into houses, flats and offices do something similar? Probably not; although some of the churches for sale do indeed still have graveyards attached, the churches themselves, whether used or not, are utterly familiar to the local people. Like the Indian burial grounds, they have, for these people, always been there, but unlike them, they have always been visible, and have far more mundane connotations. They aren’t, or weren’t just the places people got married or had funeral services, they are places where, very recently, a few times a year you trooped along with your primary school classmates to hear about the less commercial, less fun aspects of Easter or Christmas and to sing a few hymns. In short, even now churches aren’t, or are rarely “other” in the way that (to non-indigenous settlers and their descendants) Indian burial grounds are. But, after generations will they still be familiar in that way, or will they become just funny-shaped houses? Who knows, but it’s sad to think so.
Like, I’m sure, many convinced lifelong atheists (and I’m a very un-spiritual one at that), I love churches. The architecture, the fixtures and fittings, the solemn atmosphere. The idea of building on top of (Native American) Indian burial grounds was enough to fuel horror fiction and urban legend for a century; will turning churches into houses, flats and offices do something similar? Probably not; although some of the churches for sale do indeed still have graveyards attached, the churches themselves, whether used or not, are utterly familiar to the local people. Like the Indian burial grounds, they have, for these people, always been there, but unlike them, they have always been visible, and have far more mundane connotations. They aren’t, or weren’t just the places people got married or had funeral services, they are places where, very recently, a few times a year you trooped along with your primary school classmates to hear about the less commercial, less fun aspects of Easter or Christmas and to sing a few hymns. In short, even now churches aren’t, or are rarely “other” in the way that (to non-indigenous settlers and their descendants) Indian burial grounds are. But, after generations will they still be familiar in that way, or will they become just funny-shaped houses? Who knows, but it’s sad to think so.
