Another year – and the actual name of the year itself gets ever stranger and more unlikely and exotically futuristic, if you grew up in the era when the film 2001: A Space Odyssey was still set in the future. And here’s the annual attempt to get something onto this site at the beginning of the year – just made it in the first week this time – and hopefully, to post more often. The goal is a minimum of once a month but I think goals are better than resolutions so that’s as far as I will go.
 2023 was the usual mixed bag of things; I didn’t see any of the big movies of
2023 was the usual mixed bag of things; I didn’t see any of the big movies of the year yet. I have watched half of Saltburn, which so far makes me think of the early books of Martin Amis, especially Dead Babies (1975) and Success (1978) – partly because I read them again after he died last year. They are both still good/nasty/funny, especially Success, but whereas I find that having no likeable characters in a book is one thing, and doesn’t stop the book from being entertaining, watching unlikeable characters in a film is different – more like spending time with actual unlikeable people, perhaps because – especially in a film like Saltburn – you can only guess at their motivations and inner life. So, the second half of Saltburn remains unwatched – but I liked it enough that I will watch it.
the year yet. I have watched half of Saltburn, which so far makes me think of the early books of Martin Amis, especially Dead Babies (1975) and Success (1978) – partly because I read them again after he died last year. They are both still good/nasty/funny, especially Success, but whereas I find that having no likeable characters in a book is one thing, and doesn’t stop the book from being entertaining, watching unlikeable characters in a film is different – more like spending time with actual unlikeable people, perhaps because – especially in a film like Saltburn – you can only guess at their motivations and inner life. So, the second half of Saltburn remains unwatched – but I liked it enough that I will watch it.
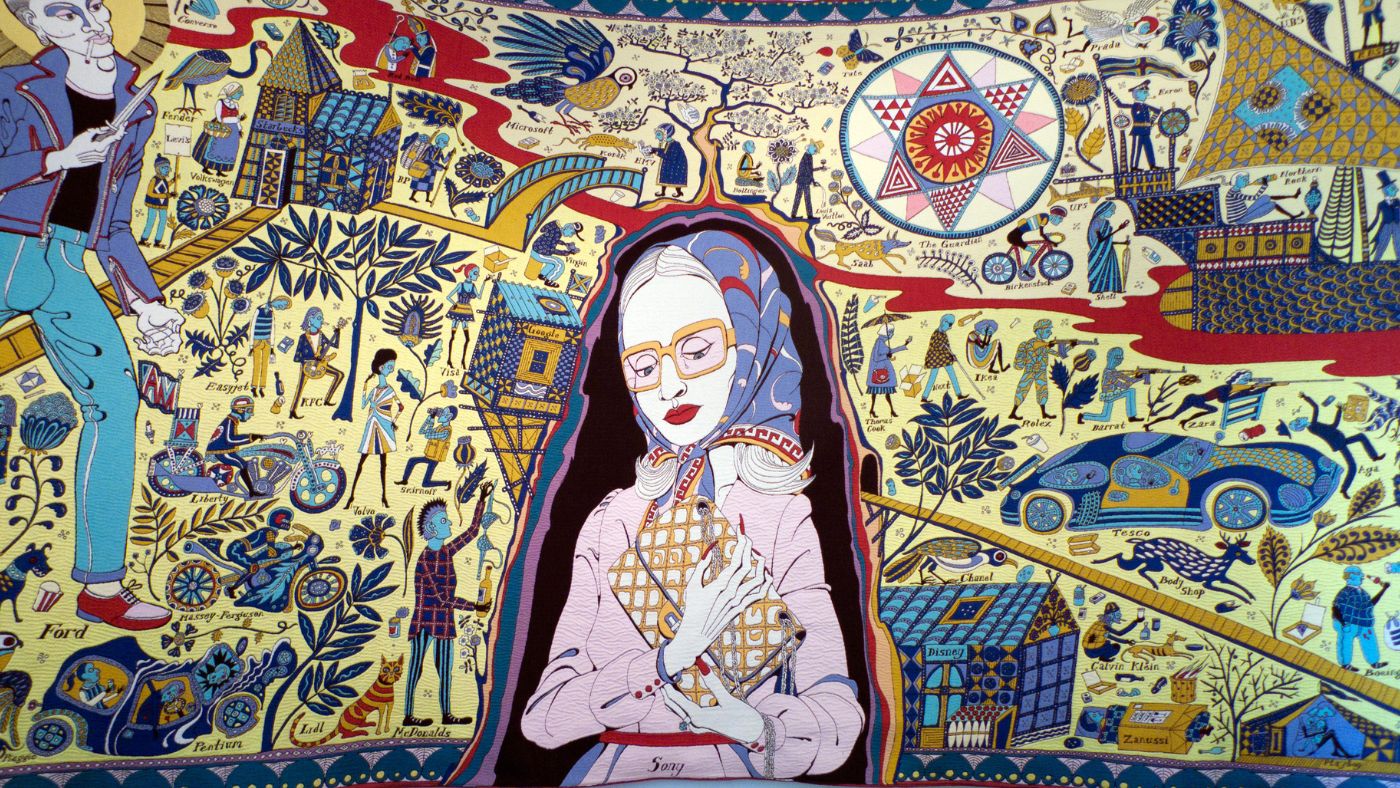

I didn’t see many exhibitions last year but am very glad that I caught Grayson Perry’s Smash Hits in Edinburgh. I didn’t really plan to see it as assumed in advance I wouldn’t like it, but in fact I loved it and ended up having a new respect for GP that only partly evaporates whenever I see him on TV.

I can’t be bothered going in depth about my favourite music of the year because the year is over and I’ve written about most it elsewhere. Old teenage favourites came back strongly: Kristin Hersh’s superb run of albums continued with Clear Pond Road. I hadn’t thought a lot about Slowdive in years but I really liked Everything is Alive and was very pleased to see them get the kind of acclaim that mostly eluded them when I was buying their first album a million years ago. Teenage Fanclub’s Nothing Lasts Forever and Drop Nineteens’ Hard Light were good too, and The Girl is Crying in her Latte by Sparks was probably my favourite of theirs outside of their early 70s classics. There were some excellent black metal (or black metal-related) albums too; much as I don’t like to think of Immortal without Abbath, Demonaz did himself proud with War Against All. Niklas Kvarforth returned to form with the brilliant Shining and Skálmöld’s Ýdalir is as good as anything they’ve recorded. In less guitar-oriented genres, I loved Kid Koala’s Creatures of the Late Afternoon and the latest Czarface record but my favourite album of the year if I had to choose one was the loveably lo-fi and enigmatic compilation Gespensterland.

 I read lots of good books in 2023 – I started keeping a list but forgot about it at some point – but the two that stand out in my memory as my favourites are both non-fiction. Lauren Elkin’s Art Monsters: Unruly Bodies in Feminist Art is completely engrossing and full of exciting ways of really looking at pictures. I wrote at length about Elena Kostyuchenko’s I Love Russia here. Kostyuchenko introduced me to a country that I only knew via history and stereotypes and her book is an exercise in what good journalism should be – informative, interesting, compassionate and readable. Both of these books cut across a wide range of subjects and examine unfamiliar things but also analyse the familiar from unfamiliar points of view; you should read them, if you haven’t already.
I read lots of good books in 2023 – I started keeping a list but forgot about it at some point – but the two that stand out in my memory as my favourites are both non-fiction. Lauren Elkin’s Art Monsters: Unruly Bodies in Feminist Art is completely engrossing and full of exciting ways of really looking at pictures. I wrote at length about Elena Kostyuchenko’s I Love Russia here. Kostyuchenko introduced me to a country that I only knew via history and stereotypes and her book is an exercise in what good journalism should be – informative, interesting, compassionate and readable. Both of these books cut across a wide range of subjects and examine unfamiliar things but also analyse the familiar from unfamiliar points of view; you should read them, if you haven’t already.
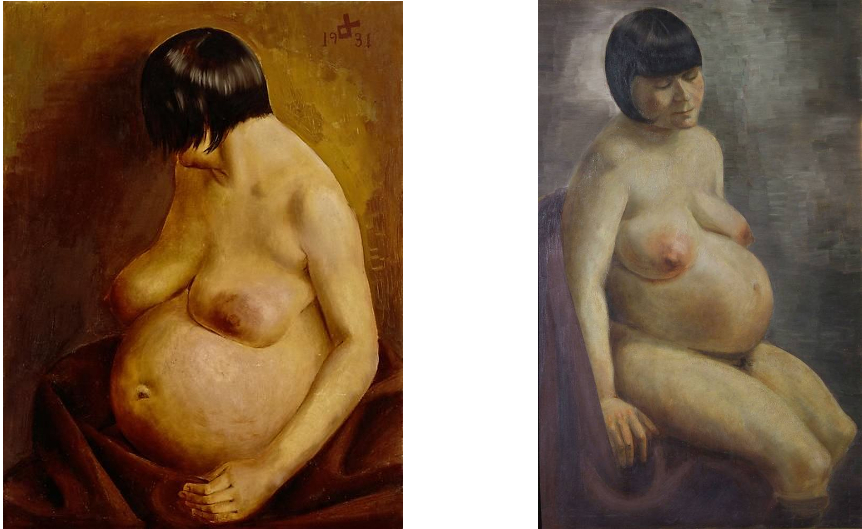
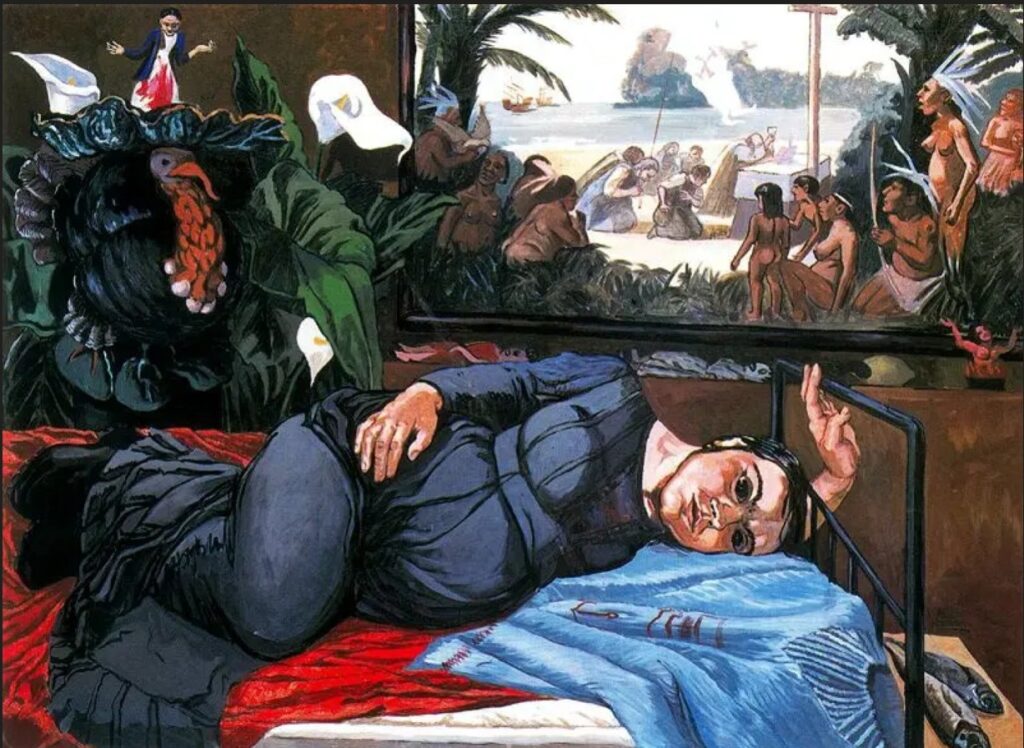
 It’s no great surprise to me that my favourite books of the year would be – like much of my favourite art – by women. Though I think the individual voice is crucial in all of the arts, individuals don’t grow in a vacuum and because female (and, more widely, non-male) voices and viewpoints have always been overlooked, excluded, marginalised and/or patronised, women and those outside of the standard, traditional male authority figures more generally, tend to have more interesting and insightful perspectives than the ‘industry standard’ artist or commentator does. The first time that thought really struck me was when I was a student, reading about Berlin Dada and finding that Hannah Höch was obviously a much more interesting and articulate artist than (though I love his work too) her partner Raoul Hausmann, but that Hausmann had always occupied a position of authority and a reputation as an innovator, where she had little-to-none. And the more you look the more you see examples of the same thing. In fact, because women occupied – and in many ways still occupy – more culturally precarious positions than men, that position informs their work – thinking for example of artists like Leonora Carrington, Kay Sage or – a bigger name now – Frida Kahlo – giving it layers of meaning inaccessible to – because unexperienced by – their male peers.
It’s no great surprise to me that my favourite books of the year would be – like much of my favourite art – by women. Though I think the individual voice is crucial in all of the arts, individuals don’t grow in a vacuum and because female (and, more widely, non-male) voices and viewpoints have always been overlooked, excluded, marginalised and/or patronised, women and those outside of the standard, traditional male authority figures more generally, tend to have more interesting and insightful perspectives than the ‘industry standard’ artist or commentator does. The first time that thought really struck me was when I was a student, reading about Berlin Dada and finding that Hannah Höch was obviously a much more interesting and articulate artist than (though I love his work too) her partner Raoul Hausmann, but that Hausmann had always occupied a position of authority and a reputation as an innovator, where she had little-to-none. And the more you look the more you see examples of the same thing. In fact, because women occupied – and in many ways still occupy – more culturally precarious positions than men, that position informs their work – thinking for example of artists like Leonora Carrington, Kay Sage or – a bigger name now – Frida Kahlo – giving it layers of meaning inaccessible to – because unexperienced by – their male peers.
The fact that women know more about themselves but also more about men than men do – because they have always had to – gives their work an emotional and intellectual charge often missing from those who belong comfortably within a tradition. This is a pretty well-worn idea – it’s why outsiders like Van Gogh or dropouts like Gauguin’s work speaks to us more clearly than the academic, tradition-bound art that they grew up with. Anybody on the margins, in whatever sense, of “mainstream society” has to have a working knowledge of that society, just to exist. Society has far less need to understand or even notice those people. – therefore their points of view are likely to not only be more individual, but more acute when it comes to observing the world in which they live. Class, race, gender; all of these things are always fascinatingly central to art and art history and the gradual recognition of that fact is making art history ever more exciting and vibrant. For now at least; we live in a time of conservative backlashes which attempt to restore order to those with a comfortable position within yesterday’s world – there will probably be an art historical backlash at some point, and the reputations of the mainstream stars of art in Van Gogh and Gauguin’s day, like William-Adolphe Bouguereau will find their reputations restored.
 If that backlash comes, it will be from the academic equivalent of those figures who, in 2023 continued to dominate the cultural landscape. These are conservative (even if theoretically radical) people who pride themselves on their superior rational, unsentimental and “common sense” outlook, but whose views tend to have a surprising amount in common with some of the more wayward religious cults. Subscribing to shallowly Darwinist ideas, but only insofar as they reinforce one’s own prejudices and somehow never feeling the need to follow them to their logical conclusions is not new, but it’s very now. Underlying ideas like the ‘survival of the fittest’, which then leads to the more malevolent idea of discouraging the “weak” in society by abolishing any kind of social structure that might support them is classic conservatism in an almost 19th century way, but somehow it’s not surprising to see these views gaining traction in the discourse of the apparently futuristic world of technology. In more that one way, these kinds of traditionalist, rigidly binary political and social philosophies work exactly like religious cults, with their apparently arbitrary cut off points for when it was that progress peaked/halted and civilisation turned bad. That point varies; but to believe things were once good but are now bad must always be problematic, because when, by any objective standards, was everything good, or were even most things good? For a certain class of British politician that point seems to have been World War Two, which kind of requires one to ignore actual World War Two. But the whole of history is infected by this kind of thinking – hence strange, disingenuous debates about how bad/how normal Empite, colonialism or slavery were; incidentially, you don’t even need to read the words of abolitionists or slaves themselves (though both would be good to read) to gain a perspective of whether or not slavery was considered ‘normal’ or bad by the standards of the time. Just look at the lyrics to Britain’s most celebratory, triumphalist song of the 18th century, Rule Britannia. James Thomson didn’t write “Britons never, never, never shall be slaves; though there’s nothing inherently wrong with slavery.” They knew it was something shameful, something to be dreaded, even while celebrating it.
If that backlash comes, it will be from the academic equivalent of those figures who, in 2023 continued to dominate the cultural landscape. These are conservative (even if theoretically radical) people who pride themselves on their superior rational, unsentimental and “common sense” outlook, but whose views tend to have a surprising amount in common with some of the more wayward religious cults. Subscribing to shallowly Darwinist ideas, but only insofar as they reinforce one’s own prejudices and somehow never feeling the need to follow them to their logical conclusions is not new, but it’s very now. Underlying ideas like the ‘survival of the fittest’, which then leads to the more malevolent idea of discouraging the “weak” in society by abolishing any kind of social structure that might support them is classic conservatism in an almost 19th century way, but somehow it’s not surprising to see these views gaining traction in the discourse of the apparently futuristic world of technology. In more that one way, these kinds of traditionalist, rigidly binary political and social philosophies work exactly like religious cults, with their apparently arbitrary cut off points for when it was that progress peaked/halted and civilisation turned bad. That point varies; but to believe things were once good but are now bad must always be problematic, because when, by any objective standards, was everything good, or were even most things good? For a certain class of British politician that point seems to have been World War Two, which kind of requires one to ignore actual World War Two. But the whole of history is infected by this kind of thinking – hence strange, disingenuous debates about how bad/how normal Empite, colonialism or slavery were; incidentially, you don’t even need to read the words of abolitionists or slaves themselves (though both would be good to read) to gain a perspective of whether or not slavery was considered ‘normal’ or bad by the standards of the time. Just look at the lyrics to Britain’s most celebratory, triumphalist song of the 18th century, Rule Britannia. James Thomson didn’t write “Britons never, never, never shall be slaves; though there’s nothing inherently wrong with slavery.” They knew it was something shameful, something to be dreaded, even while celebrating it.
But anyways, the kind of avowedly forward-looking people we that are saddled with now, with their apparent concern for the future of the human species – especially the wellbeing of thus far non-existent future humans, as opposed to actual real living humans are, unlike the Amish, okay with progress, in the material sense of cars, computers, aircraft, spacecraft. But that only makes their core concern with traditional values and what is natural/unnatural even more nonsensical. If the defining thing about human beings is nature – men are like this, but not like that, women are like that, but not this; that nature dictates that compassion and medical science ate wasted on the weak and inferior, etc, then why draw the line at controlling gender and reproduction? Why get excited about the use of vaccines, or whether or not people “should” eat meat? If nature/”natural” really is the be all end all of human existence, why wear clothes, drive cars, cook food, use computers, build houses? At what point does nature dictate what we do or can or should do? Isn’t everything humans do inherently natural because we have the capacity to do it and actually do do it?
Again, despite the supposed rationalism that fuels the superiority complexes of so many powerful people in whatever sector, their bullshit traditional ideas are dictated against – and always have been – by the lived experience of almost everyone in the world. If ‘real men’ are strong, rational and above all heterosexual, how come most of us will have met, throughout our lives, emotional, irrational men who can’t cope with pressure, who aren’t in control of themselves or their environment? How come homosexuality has existed since the beginning of recorded time and does not go away no matter how traditional or repressive society becomes or how much generation after generation insists that it is unnatural? If ‘real women’ are weak, gentle, sentimental, maternal, submissive and above all heterosexual, how come (etc, etc, etc, etc) Because of decadent western society? Well Western society is partly founded on the ideas of Ancient Greece, which though pretty misogynistic, famously did not have quite the same views on sexuality. And how come these people equally exist in every other society too? Could it be that traditional ideas of ‘human nature’ have nothing to do with actual nature but have always existed in western patriarchal societies simply to reinforce the status quo in the interests of those at the top of the hierarchical tree? From monarchies to oligarchies to modern democracies and communist states – all of which have their own ruling class, even when it is explicitly labelled otherwise – it’s been in the interest of those in charge to prevent anything which fundamentally changes the way things work.
For similar reasons, people in western society (perhaps elsewhere; I am no expert) who live unremarkable and mediocre lives within essentially complacent, and often apolitical circles are increasingly drawn to right rather than left wing extremism to gain prominence and (importantly) material success. Extremist views across the spectrum are entertainingly “edgy” and titillating to people who like to be entertained by controversy and/or shocked by outrageous behaviour, but right-wing views are far more acceptable within the media – and therefore are far more lucrative and rewarding – because they don’t threaten the financial basis that underpins the media and political structure.
So in short – only joking, this will be a long sentence (deep breath). If comedian or podcaster A) gains millions of followers who are excited about disruptive ideas that undermine the state by questioning the validity of the (sigh) mainstream media, by interrogating ideas of media ownership and the accumulation of wealth and power and so on, that represents a genuine threat to Rupert Murdoch, Viscount Rothermere, Meta and Elon Musk in a way that comedian or podcaster B), gaining millions of followers who lean towards ideas that disrupt society by attacking progressive, egalitarian or (sigh) “woke” culture does not. Regardless of the actual or avowed political beliefs of these media magnates, is comedian/podcaster A or comedian/podcaster B going to be the one they champion in order to tap into the zeitgeist (which media magnates have to do to survive)?
BUT ANYWAY, it would be nice to think that these things would be less central or at least more ignorable in 2024. It would also be nice if people in power could not enable the worst elements in society (where the two things are separable). It would be more than nice if the governments of the world would listen to people and end the butchering of helpless civilians. It’s important to remember that it is in the interests of governments – even relatively benign ones – that people in general feel powerless. But we’re not. If making resolutions works for you then make them, if not then don’t, if you have goals then aim for those and you may achieve something even if not everything you want to achieve. But if something is unacceptable to you, don’t accept it. You may have money, power, time or you may have little more than your own body and/or your own mind, but those are 100% yours and the most important things of all. Happy New Year and good luck!














 It’s funny; the arrogance and certainty of youth is well-known, but I’m still very surprised to find it in myself. I have rarely met anyone less sure of themselves or more reticent than my late-teens/early-20s self, but that doesn’t come across at all, except in a few deliberately self-deprecating caveats, and there’s an infuriating cockiness to some of the writing that I not only don’t identify with, but really hate; what’s mortifying is that I was genuinely trying to think deeply about the issues I covered so shallowly. Oh well, I hope I wasn’t actually that obnoxious in everyday life, but who knows? (anyone who knew me). On the other hand, my actual views don’t seem to have changed as much as I would have expected. I was more of a libertarian, albeit a left-wing one then, perhaps a bit more pessimistic, but on the whole I would still find myself on the same side of most of the arguments I am making, which is reassuring.
It’s funny; the arrogance and certainty of youth is well-known, but I’m still very surprised to find it in myself. I have rarely met anyone less sure of themselves or more reticent than my late-teens/early-20s self, but that doesn’t come across at all, except in a few deliberately self-deprecating caveats, and there’s an infuriating cockiness to some of the writing that I not only don’t identify with, but really hate; what’s mortifying is that I was genuinely trying to think deeply about the issues I covered so shallowly. Oh well, I hope I wasn’t actually that obnoxious in everyday life, but who knows? (anyone who knew me). On the other hand, my actual views don’t seem to have changed as much as I would have expected. I was more of a libertarian, albeit a left-wing one then, perhaps a bit more pessimistic, but on the whole I would still find myself on the same side of most of the arguments I am making, which is reassuring.





 My favourite album of that year was Ihsahn’s Das Seelenbrechen, and it’s still one of my favourite albums. I rarely listen to it all the way through at the moment, but various tracks, such as Pulse, Regen and NaCL are still in regular rotation
My favourite album of that year was Ihsahn’s Das Seelenbrechen, and it’s still one of my favourite albums. I rarely listen to it all the way through at the moment, but various tracks, such as Pulse, Regen and NaCL are still in regular rotation My favourite album of 2014 was
My favourite album of 2014 was My album of 2015 was Life is a Struggle, Give Up by
My album of 2015 was Life is a Struggle, Give Up by 
 I wouldn’t necessarily say I was aware of it at the time, but 2016 was a great year for music. My album of the year was Wyatt at the Coyote Palace by Kristin Hersh (which I enthused about
I wouldn’t necessarily say I was aware of it at the time, but 2016 was a great year for music. My album of the year was Wyatt at the Coyote Palace by Kristin Hersh (which I enthused about
 2017 had fewer standouts for me but my album of the year, the self-titled debut by Finnish alt-rock band Ghost World, which I wrote enthusiastically about
2017 had fewer standouts for me but my album of the year, the self-titled debut by Finnish alt-rock band Ghost World, which I wrote enthusiastically about  I was hugely surprised in 2018 to find that my album of the year was an electronic one,
I was hugely surprised in 2018 to find that my album of the year was an electronic one,  In 2019, I loved another Collectress album, Different Geographies but it didn’t replace or match Mondegreen in my affections. I can’t seem to find my album of the year strangely, but it might well have been Youth in Ribbons by Revenant Marquis, still my favourite of that prolific artist’s releases.
In 2019, I loved another Collectress album, Different Geographies but it didn’t replace or match Mondegreen in my affections. I can’t seem to find my album of the year strangely, but it might well have been Youth in Ribbons by Revenant Marquis, still my favourite of that prolific artist’s releases.
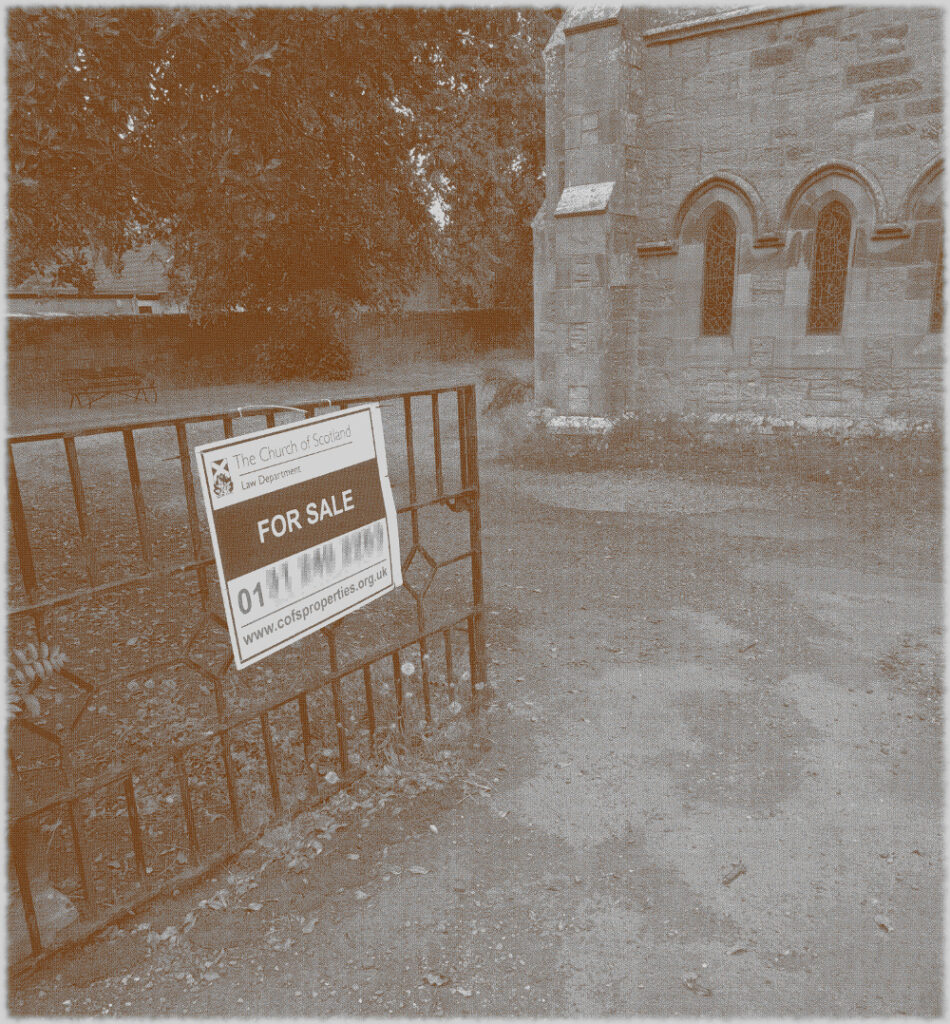
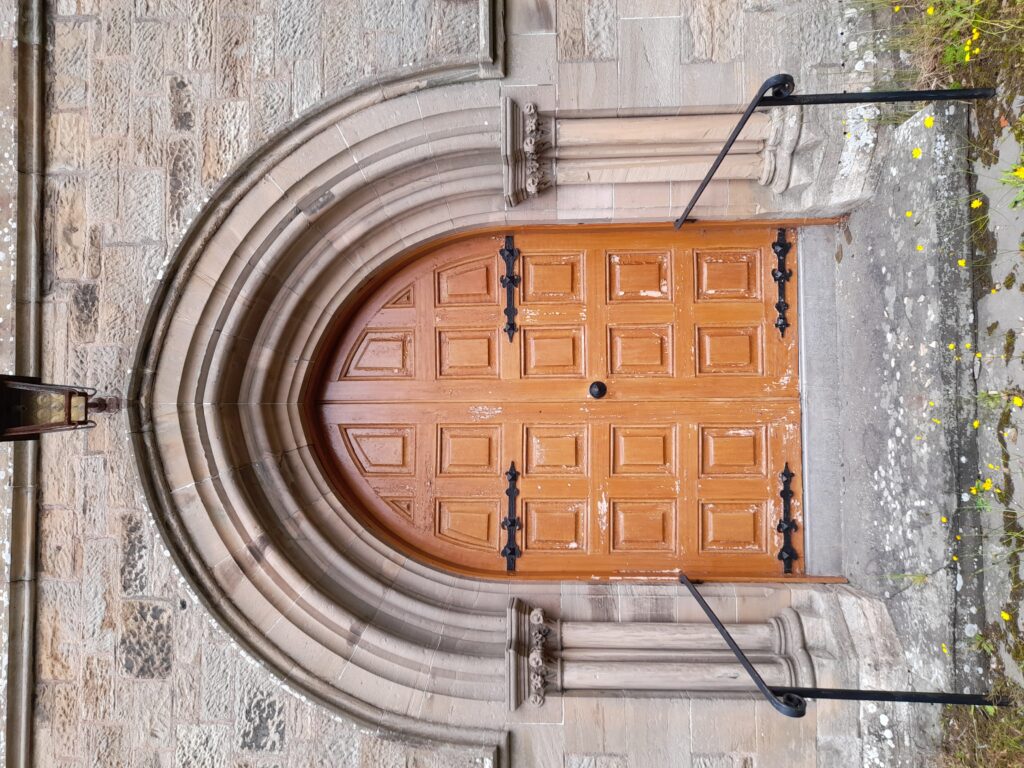
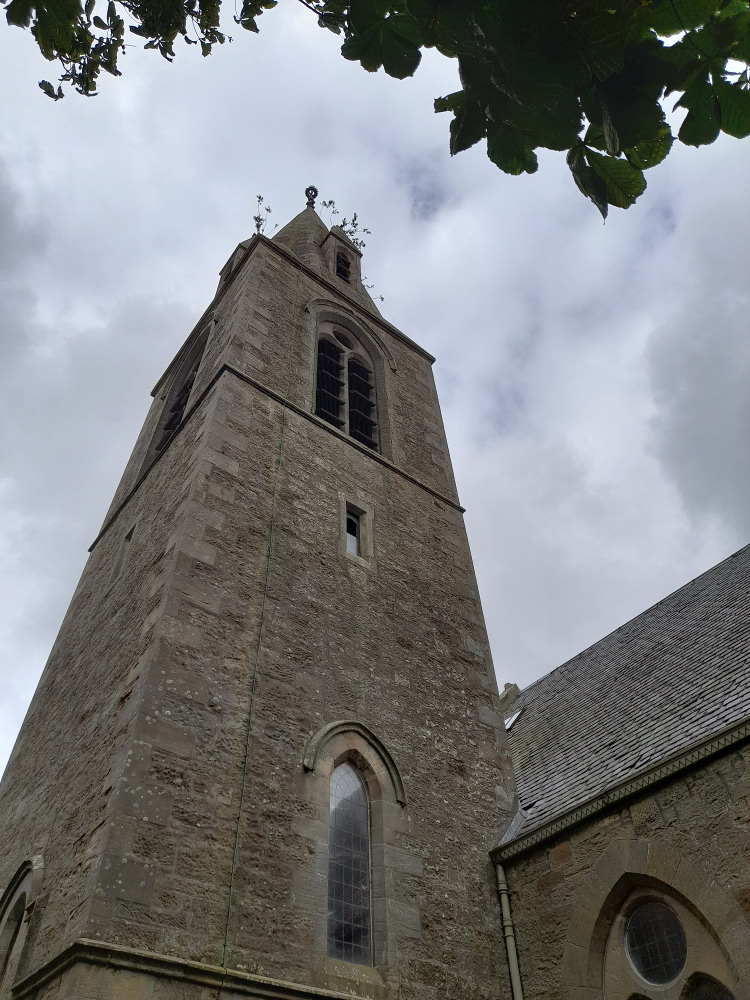













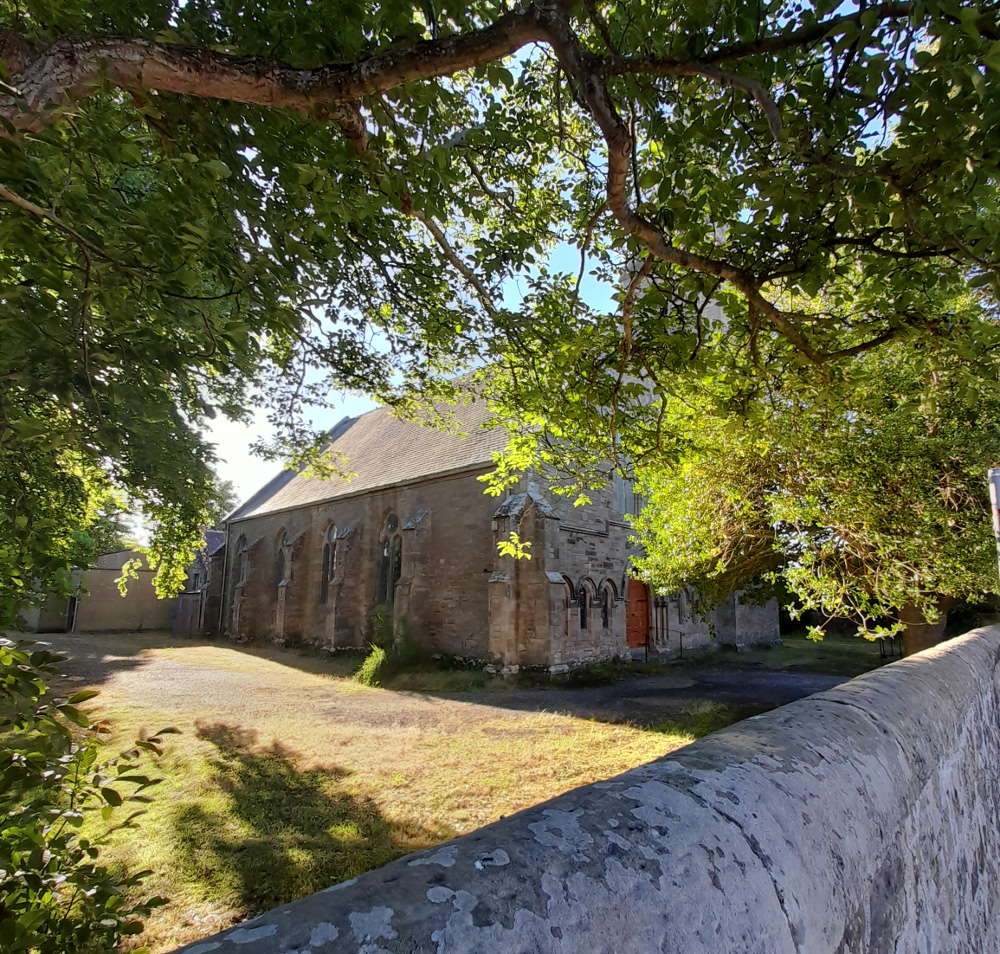
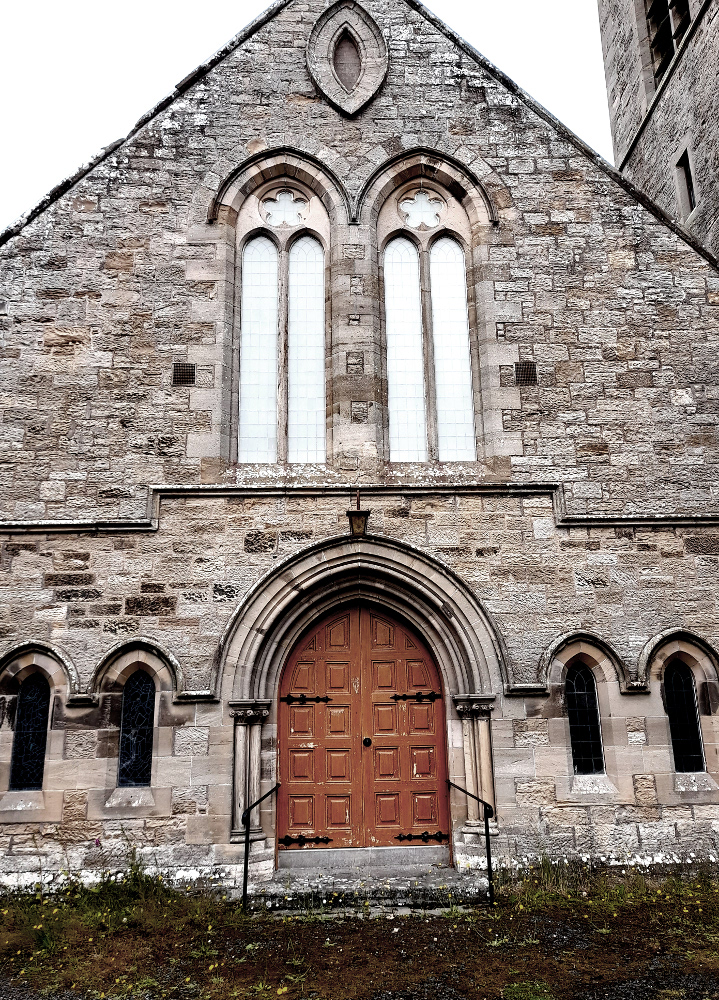
 The idea that money is more important to the Church of Scotland than the buildings that were at the centre of the spiritual and social lives of generations of people (and also, the place that God lived, I guess) seems grotesque, but there it is. It’s just bricks (or stone) and mortar, after all; or that, presumably is the logic, because God doesn’t actually live in a stone building but in either heaven or the hearts of believers etc, etc. And yet, if it’s just a building, how come people can only vandalise houses or schools or barns, but they can “desecrate” churches? “De-consecration” – what the church does in order to render its buildings saleable – is just a non-inflammatory way of saying desecration. De-consecrating the church doesn’t affect the material of the building, but it does remove its purpose – but what it can’t do is remove its history. So if you buy a church, what is it that are you actually buying? In a book I liked as a teenager, Terry Brooks’s Magic Kingdom For Sale – Sold! (1986), a depressed lawyer called Ben Holiday buys what turns out to be something like Narnia or Middle Earth, from a catalogue (nowadays it would be from a website). If Mr Holiday bought a church, he wouldn’t be mystically transported to an otherworldly realm, but he would – and the buyers of these buildings do – become the owner of a place where thousands of people were, in a meaningful way, transported to a place where, whatever the privations and terrors of their daily lives might be, things made some sort of black-and-white sense. Somewhere that virtue was rewarded with eternal paradise, vice was punished with eternal damnation and the person in the pulpit had the correct answers to whatever questions life was throwing at you. You don’t have to believe in any of that to realise that it was (and to some extent I suppose still is) important.
The idea that money is more important to the Church of Scotland than the buildings that were at the centre of the spiritual and social lives of generations of people (and also, the place that God lived, I guess) seems grotesque, but there it is. It’s just bricks (or stone) and mortar, after all; or that, presumably is the logic, because God doesn’t actually live in a stone building but in either heaven or the hearts of believers etc, etc. And yet, if it’s just a building, how come people can only vandalise houses or schools or barns, but they can “desecrate” churches? “De-consecration” – what the church does in order to render its buildings saleable – is just a non-inflammatory way of saying desecration. De-consecrating the church doesn’t affect the material of the building, but it does remove its purpose – but what it can’t do is remove its history. So if you buy a church, what is it that are you actually buying? In a book I liked as a teenager, Terry Brooks’s Magic Kingdom For Sale – Sold! (1986), a depressed lawyer called Ben Holiday buys what turns out to be something like Narnia or Middle Earth, from a catalogue (nowadays it would be from a website). If Mr Holiday bought a church, he wouldn’t be mystically transported to an otherworldly realm, but he would – and the buyers of these buildings do – become the owner of a place where thousands of people were, in a meaningful way, transported to a place where, whatever the privations and terrors of their daily lives might be, things made some sort of black-and-white sense. Somewhere that virtue was rewarded with eternal paradise, vice was punished with eternal damnation and the person in the pulpit had the correct answers to whatever questions life was throwing at you. You don’t have to believe in any of that to realise that it was (and to some extent I suppose still is) important.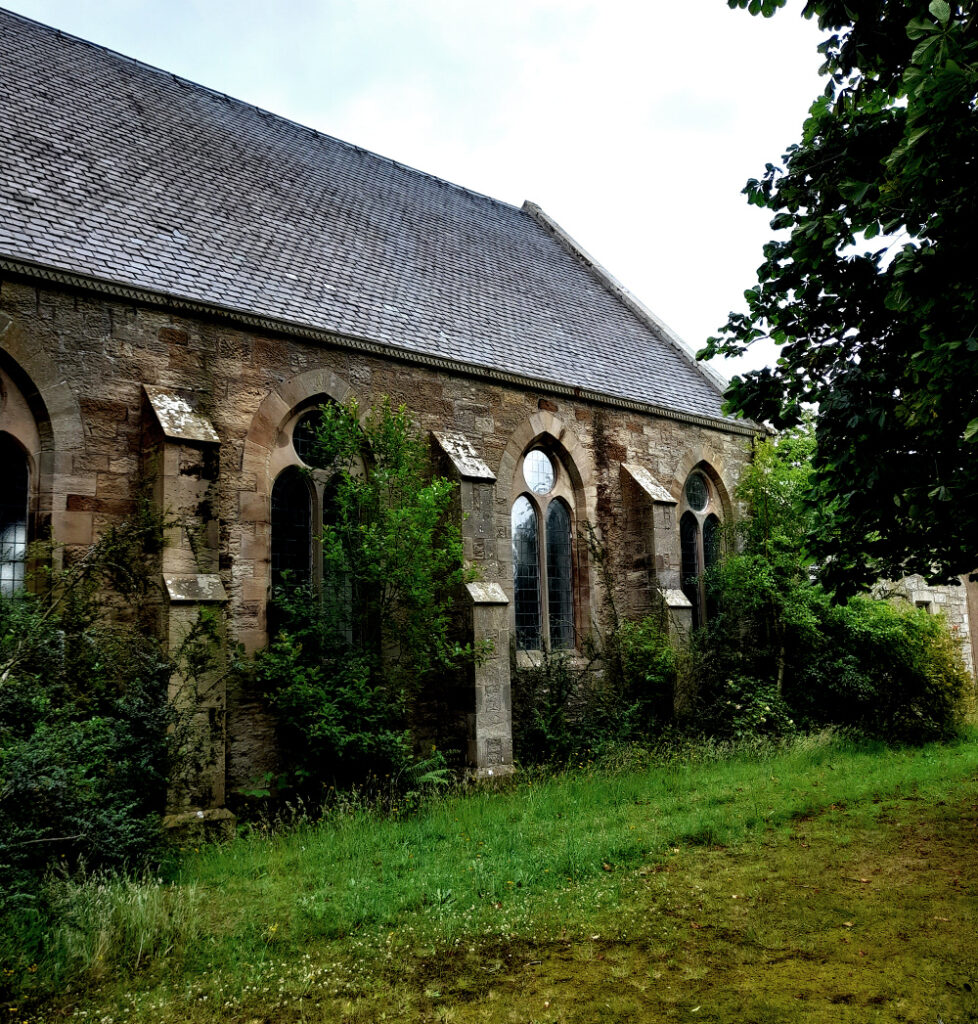 Like, I’m sure, many convinced lifelong atheists (and I’m a very un-spiritual one at that), I love churches. The architecture, the fixtures and fittings, the solemn atmosphere. The idea of building on top of (Native American) Indian burial grounds was enough to fuel horror fiction and urban legend for a century; will turning churches into houses, flats and offices do something similar? Probably not; although some of the churches for sale do indeed still have graveyards attached, the churches themselves, whether used or not, are utterly familiar to the local people. Like the Indian burial grounds, they have, for these people, always been there, but unlike them, they have always been visible, and have far more mundane connotations. They aren’t, or weren’t just the places people got married or had funeral services, they are places where, very recently, a few times a year you trooped along with your primary school classmates to hear about the less commercial, less fun aspects of Easter or Christmas and to sing a few hymns. In short, even now churches aren’t, or are rarely “other” in the way that (to non-indigenous settlers and their descendants) Indian burial grounds are. But, after generations will they still be familiar in that way, or will they become just funny-shaped houses? Who knows, but it’s sad to think so.
Like, I’m sure, many convinced lifelong atheists (and I’m a very un-spiritual one at that), I love churches. The architecture, the fixtures and fittings, the solemn atmosphere. The idea of building on top of (Native American) Indian burial grounds was enough to fuel horror fiction and urban legend for a century; will turning churches into houses, flats and offices do something similar? Probably not; although some of the churches for sale do indeed still have graveyards attached, the churches themselves, whether used or not, are utterly familiar to the local people. Like the Indian burial grounds, they have, for these people, always been there, but unlike them, they have always been visible, and have far more mundane connotations. They aren’t, or weren’t just the places people got married or had funeral services, they are places where, very recently, a few times a year you trooped along with your primary school classmates to hear about the less commercial, less fun aspects of Easter or Christmas and to sing a few hymns. In short, even now churches aren’t, or are rarely “other” in the way that (to non-indigenous settlers and their descendants) Indian burial grounds are. But, after generations will they still be familiar in that way, or will they become just funny-shaped houses? Who knows, but it’s sad to think so.